Difference between revisions of "2020 DOCK tutorial 3 with PDBID 4F4P"
Stonybrook (talk | contribs) (→Generating Grid) |
Stonybrook (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
grid -i grid.in -o grid.out | grid -i grid.in -o grid.out | ||
| + | |||
| + | =V. Energy Minimization= | ||
Revision as of 14:55, 19 February 2020
This tutorial teaches you how to dock a drug molecule to a receptor.
/*This page is under construction*/
Contents
I. Introduction
DOCK
DOCK is an important molecular docking program in molecular modeling and drug design. It enables you to dock a small molecule (ligand) to a binding pocket of certain protein target (receptor) and find out correct binding geometry, types and number of interactions involve in binding and energies associate with binding. For this tutorial DOCK6.9 package was used. Purpose of using DOCK6.9 in this tutorial is to re-dock a ligand to a binding pocket of the receptor protein for pose reproduction and find out lead compounds which have stronger binding affinity with our receptor binding site.
Virtual Screening
This is a protocol widely used in drug design which enable you to find out small molecules that have higher binding affinity with the binding pocket of protein of interest by screening a millions of compounds in a virtual database (such as ZINC).
Organization of directories
Log in to the seawulf cluster and go to your group directory. Use following command to create files.
mkdir 001.files 002.surface_spheres 003.gridbox 004.dock 005.virtual_screen 006.virtual_screen_mpi 007.cartesianmin 008.rescore
4F4P
4F4P is the crystal structure of Tyrosine Kinase SYK in complex with ligand LASW836. You can get the pdb file from here [1]. The resolution is 2.37 Å. Click Download Files -> PDB Format to download PDB file.
II. Preparation of the ligand and receptor
Checking the structure
Read the article related to the PDB file [2] to understand protonation states, charges and other important information regarding the receptor and the ligand.
Open the pdb file through chimera and look at the structure.
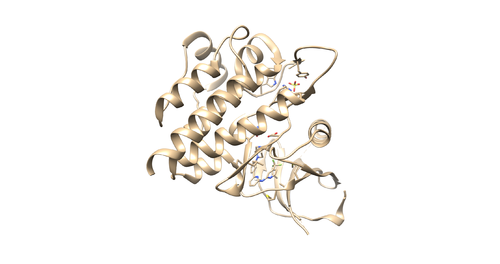
Identify the main components of the model (receptor, ligand, solvent, cofactors). In our case, the PDB file contains one protein chain, ligand(OSB), sulfate ion(SO4(2-)) as a cofactor and water molecules (H2O).
Next, we are going to generate the receptor file and the ligand file.
Prepare the Receptor file
With the PDB file loaded by chimera, do Select -> Residue -> SO4 to select the sulfate. Use Actions -> Atoms/Bonds -> Delete to delete it. Then do Select -> Residue -> HOH to select the water molecules. Use the same method to delete it. Then do Select -> Structure -> (0SB) to select ligand molecule. Use the same method to delete it. Save the receptor as 4f4p_rec_noh.mol2.
OR
With the PDB file loaded by chimera, hold the control button and click on the protein chain to select a protein residue. Then click up arrow button to select the whole protein chain (Receptor). Then Select -> Invert(all models) to invert your selection (This will select all the components in your PDB file except receptor). Then do Actions->Atoms/bonds->Delete. You will remain with a protein receptor. Save the receptor as 4f4p_rec_noh.mol2.
Prepare the Ligand File
Open the pdf file again. Do Select -> Structure -> ligand(0SB) to select the ligand. Do Select -> Invert (all models), then delete the selected atoms. This will left the ligand molecule only. Save it as 4f4p_lig_noh.mol2.
Adding hydrogen and charge
Now we are going to add hydrogen atoms and charges to our receptor and ligand. Open 4f4p_rec_noh.mol2 file using Chimera and use the following instructions to prepare the receptor file to be used in DOCK. Tools -> Structure editing -> AddH. This command will add hydrogen to the receptor. Tools -> Structure editing -> Add Charge. This command will add charge to atoms to make the receptor neutral. Save the file as 4f4p_rec_h.mol2
Open 4f4p_lig_noh.mol2, follow the same steps for ligand file, add hydrogen. The Chimera added 2 hydrogens to the nitrogen where it is supposed to be only one, as referred in the pdb report. So remove one hydrogen.
(Hold Ctrl and select extra H, then Actions -> Atoms/Bonds -> delete.) (Therefore, Be really concern when adding Hydrogens using chimera since it is automatically adding unwanted hydrogen atoms. Compare your protonation state with PDB report and make sure you have correct structure after adding hydrogens.)
After removing hydrogen add charges to the ligand
Tools -> Structure editing -> Add Charge. After this save the file as 4f4p_lig_h.mol2.
copy the 4f4p_rec_h.mol2, 4f4p_rec_noh.mol2, 4f4p_lig_noh.mol2, 4f4p_lig_h.mol2 files in to 001.files directory
III. Generating receptor surface and spheres
Creating a surface (DMS) file
Open the 4f4p_rec_noh.mol2 file in chimera. Then Action -> surface -> show -> Shows the surface of the receptor without H.
Tools -> Structure editing -> write DMS -> name: 4f4p_rec_noh.dms -> This command saves the surface of the receptor in dms format.
copy the 4f4p_rec.dms file in to 002.surface_spheres directory.
Generating spheres
Go to 002.surface_spheres folder Create a new input file to create spheres by
vi INSPH
then type the following lines inside the file.
4f4p_rec_noh.dms R X 0.0 4.0 1.4 4f4p_rec.sph
The first line 4f4p_rec_noh.dms specifies the input file. R indicates that spheres generated will be outside of the receptor surface. X specifies all the points will be used. 0.0 is the distance in angstroms and it will avoid steric clashes. 4.0 is the maximum surface radius of the spheres and 1.4 is the minimum radius in angstroms.The last line 4f4p_rec.sph creates the sph file that contains clustered spheres.
Once the INSPH file is ready, type the following command to generate the spheres.
sphgen -i INSPH -o OUTSPH
Once sphgen command is successful, 4f4p_rec.sph file will be created. Open it up using Chimera along with 4f4p_rec_noh.mol2 file. You should get a similar output like the image below.
Selecting Spheres
Here we will be selecting the spheres which defines the binding pocket of the ligand because we are trying to direct the ligand towards that binding site rather than all over the receptor. To select the spheres type the following command.
sphere_selector 4f4p_rec.sph ../001.files/4f4p_noh_lig.mol2 10.0
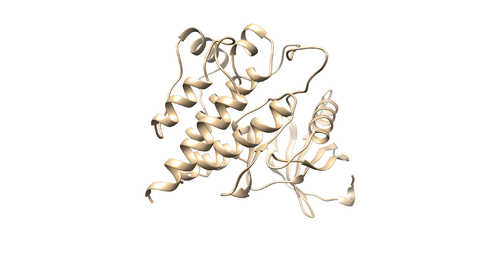
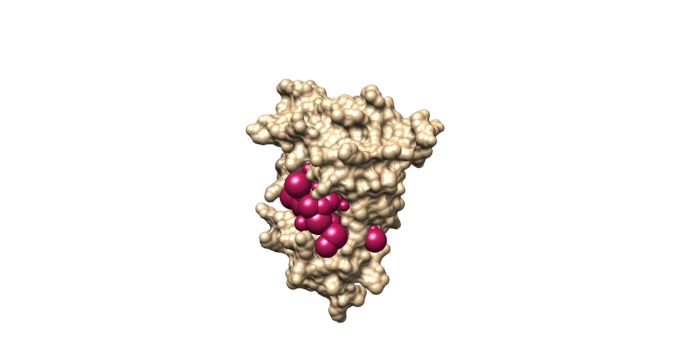
This command will select all of the spheres within 10.0 angstroms of the ligand and output them to selected_spheres.sph. Visualize the selected spheres using Chimera to make sure the correct spheres are selected. Notice that, spheres around the ligand binding site are kept and all the other spheres are deleted in the image below.
IV. Generating box and grid
Generating box
Move to 003.gridbox directory Create a new file showbox.in and write the following lines in the file(# means comment ).
Y. #Say 'Yes' to make a box 8.0 #The boundary of the box is at least 8 Angstroms from any spheres ../002.surface_spheres/selected_spheres.sph. #The location and file name of the sphere file 1 #Use the first cluster of spheres (only 1 cluster in this case) 4f4p.box.pdb. #The output filename
Generating Grid
Create a new input file called grid.in and write the following information there.
compute_grids yes grid_spacing 0.4 output_molecule no contact_score no energy_score yes energy_cutoff_distance 9999 atom_model a attractive_exponent 6 repulsive_exponent 9 distance_dielectric yes dielectric_factor 4 bump_filter yes bump_overlap 0.75 receptor_file ../001.files/4f4p_rec_h.mol2 box_file 4f4p.box.pdb vdw_definition_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.9_release/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn score_grid_prefix grid
save the file and run the following command.
grid -i grid.in -o grid.out