Difference between revisions of "2023 DOCK tutorial 3 with PDBID 2P16"
Stonybrook (talk | contribs) (→Grid Generation) |
BrockBoysan (talk | contribs) (→Grid Generation) |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
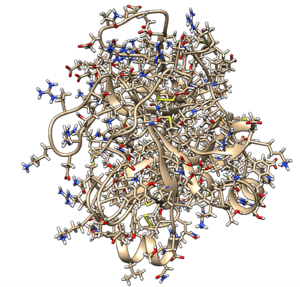
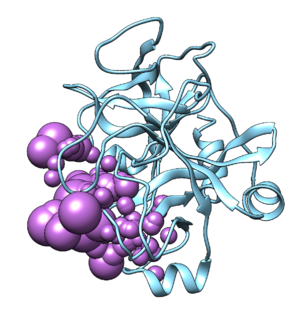
Make sure you read the associated paper to get an understanding protonation states, charges, and crystallization conditions. Identify the following components- protein, ligand, ions, and solvent. | Make sure you read the associated paper to get an understanding protonation states, charges, and crystallization conditions. Identify the following components- protein, ligand, ions, and solvent. | ||
| − | [[File:2p16. | + | [[File:2p16.png|thumb|center]] |
We will be assuming biological pH and neglecting solvent and ion effects, so you can delete the ions, solvent, and protein chain that isn't involved in ligand binding using the following Chimera commands: | We will be assuming biological pH and neglecting solvent and ion effects, so you can delete the ions, solvent, and protein chain that isn't involved in ligand binding using the following Chimera commands: | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
Save the file as 2p16_cleaned.pdb | Save the file as 2p16_cleaned.pdb | ||
| − | [[File:2p16_cleaned. | + | [[File:2p16_cleaned.png|thumb|center]] |
=== '''Protein Preparation''' === | === '''Protein Preparation''' === | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
Save the file as 2p16_noh_protein.mol2 using File-> Save Mol2 | Save the file as 2p16_noh_protein.mol2 using File-> Save Mol2 | ||
| − | [[File:2p16_noh_protein. | + | [[File:2p16_noh_protein.png|thumb|center]] |
To add hydrogens and charge, you may use the Dockprep function in Chimera through Tools->Surface/Binding Analysis->Dock Prep. Uncheck delete solvent in the first window, as we have done this manually, and press ok until you reach the "Assign Charges" window. Ensure that AMBER ff14SB is selected in this window and AM1-BCC in the following "Specify Net Charges" window. Save the file as 2p16_dockprep_protein.mol2 | To add hydrogens and charge, you may use the Dockprep function in Chimera through Tools->Surface/Binding Analysis->Dock Prep. Uncheck delete solvent in the first window, as we have done this manually, and press ok until you reach the "Assign Charges" window. Ensure that AMBER ff14SB is selected in this window and AM1-BCC in the following "Specify Net Charges" window. Save the file as 2p16_dockprep_protein.mol2 | ||
| − | [[File:2p16_dockprep_protein. | + | [[File:2p16_dockprep_protein.png|thumb|center]] |
=== '''Ligand Preparation''' === | === '''Ligand Preparation''' === | ||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
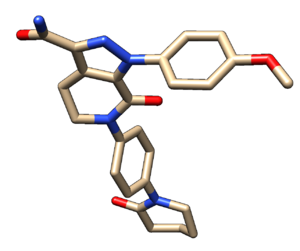
Save the file as 2p16_noh_ligand.mol2 using File-> Save Mol2 | Save the file as 2p16_noh_ligand.mol2 using File-> Save Mol2 | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:2p16nohligand.png|thumb|center]] |
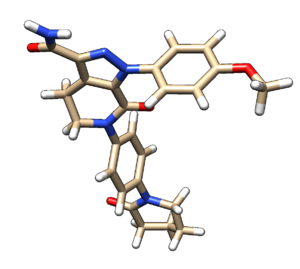
Add hydrogens and charge using Dockprep. Save the file as 2p16_dockprep_ligand.mol2 | Add hydrogens and charge using Dockprep. Save the file as 2p16_dockprep_ligand.mol2 | ||
| − | [[File:2p16_dockprep_ligand. | + | [[File:2p16_dockprep_ligand.png|thumb|center]] |
== '''Surface Spheres''' == | == '''Surface Spheres''' == | ||
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
Save the file as 2p16_noh_protein.dms | Save the file as 2p16_noh_protein.dms | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== '''Sphere Generation''' === | === '''Sphere Generation''' === | ||
| Line 145: | Line 143: | ||
<pre>sphgen -i INSPH -o OUTSPH</pre> | <pre>sphgen -i INSPH -o OUTSPH</pre> | ||
| − | Open your output file 2p16_protein. | + | Open your output file 2p16_protein.sph along with your 2016_noh_protein.mol2 file to check if everything looks ok. |
| − | [[File:2p16_spheres. | + | [[File:2p16_spheres.png|thumb|center]] |
=== '''Sphere Selection''' === | === '''Sphere Selection''' === | ||
| Line 157: | Line 155: | ||
<pre>sphere_selector 2p16_protein.sph ../structures/2p16_noh_ligand.mol2 10.0</pre> | <pre>sphere_selector 2p16_protein.sph ../structures/2p16_noh_ligand.mol2 10.0</pre> | ||
| − | [[File:2p16_selected_spheres. | + | [[File:2p16_selected_spheres.png|thumb|center]] |
== '''Grid Box''' == | == '''Grid Box''' == | ||
| Line 177: | Line 175: | ||
<pre>showbox < showbox.in</pre> | <pre>showbox < showbox.in</pre> | ||
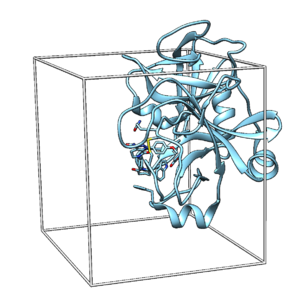
| − | [[File:2p16_gridbox. | + | [[File:2p16_gridbox.png|thumb|center]] |
=== '''Grid Generation''' === | === '''Grid Generation''' === | ||
Open up an input file titled grid.in and type in the following: | Open up an input file titled grid.in and type in the following: | ||
| − | + | <pre>allow_non_integral_charges no | |
| − | <pre>compute_grids yes | + | compute_grids yes |
grid_spacing 0.4 | grid_spacing 0.4 | ||
output_molecule no | output_molecule no | ||
| Line 198: | Line 196: | ||
receptor_file ../structures/2p16_dockprep_protein.mol2 | receptor_file ../structures/2p16_dockprep_protein.mol2 | ||
box_file 2p16.box.pdb | box_file 2p16.box.pdb | ||
| − | vdw_definition_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn | + | vdw_definition_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn |
score_grid_prefix grid</pre> | score_grid_prefix grid</pre> | ||
| Line 209: | Line 207: | ||
=== '''Ligand Minimization''' === | === '''Ligand Minimization''' === | ||
| − | Before running DOCK we need to ensure our ligand is energy minimized to prevent any steric clashes. | + | Before running DOCK we need to ensure our ligand is energy minimized to prevent any steric clashes. |
| + | |||
| + | Switch to the dock directory and open up an input file called min.in and type in the following: | ||
<pre>conformer_search_type rigid | <pre>conformer_search_type rigid | ||
| Line 256: | Line 256: | ||
simplex_coefficient_restraint 10.0 | simplex_coefficient_restraint 10.0 | ||
atom_model all | atom_model all | ||
| − | vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn | + | vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn |
| − | flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6/parameters/flex.defn | + | flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn |
| − | flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6/parameters/flex_drive.tbl | + | flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl |
| − | ligand_outfile_prefix | + | ligand_outfile_prefix 2p16_ligand.min |
write_orientations no | write_orientations no | ||
num_scored_conformers 1 | num_scored_conformers 1 | ||
rank_ligands no</pre> | rank_ligands no</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Run the minimization using: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre>dock6 -i min.in -o min.out</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This should save a new file called 2p16_ligand.min_scored.mol2. Open it up in Chimera along with the protein and ligand mol2 files for comparison. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:2p16ligandminscored.png|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can also view the RMSD values in the header of the file using: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre>head 2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2</pre> | ||
=='''Footprint Analysis'''== | =='''Footprint Analysis'''== | ||
| + | |||
| + | We can use footprinting to visualize the protein-ligand interaction energies on a per-residue basis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the same dock directory open up an input file called footprint.in and type in the following: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre>conformer_search_type rigid | ||
| + | use_internal_energy no | ||
| + | ligand_atom_file 2p16_ligand.min_scored.mol2 | ||
| + | limit_max_ligands no | ||
| + | skip_molecule no | ||
| + | read_mol_solvation no | ||
| + | calculate_rmsd no | ||
| + | use_database_filter no | ||
| + | orient_ligand no | ||
| + | bump_filter no | ||
| + | score_molecules yes | ||
| + | contact_score_primary no | ||
| + | contact_score_secondary no | ||
| + | grid_score_primary no | ||
| + | grid_score_secondary no | ||
| + | multigrid_score_primary no | ||
| + | multigrid_score_secondary no | ||
| + | dock3.5_score_primary no | ||
| + | dock3.5_score_secondary no | ||
| + | continuous_score_primary no | ||
| + | continuous_score_secondary no | ||
| + | footprint_similarity_score_primary yes | ||
| + | footprint_similarity_score_secondary no | ||
| + | fps_score_use_footprint_reference_mol2 yes | ||
| + | fps_score_footprint_reference_mol2_filename ../structures/2p16_dockprep_ligand.mol2 | ||
| + | fps_score_foot_compare_type Euclidean | ||
| + | fps_score_normalize_foot no | ||
| + | fps_score_foot_comp_all_residue yes | ||
| + | fps_score_receptor_filename ../structures/2p16_dockprep_protein.mol2 | ||
| + | fps_score_vdw_att_exp 6 | ||
| + | fps_score_vdw_rep_exp 9 | ||
| + | fps_score_vdw_rep_rad_scale 1 | ||
| + | fps_score_use_distance_dependent_dielectric yes | ||
| + | fps_score_dielectric 4.0 | ||
| + | fps_score_vdw_fp_scale 1 | ||
| + | fps_score_es_fp_scale 1 | ||
| + | fps_score_hb_fp_scale 0 | ||
| + | pharmacophore_score_secondary no | ||
| + | descriptor_score_secondary no | ||
| + | gbsa_zou_score_secondary no | ||
| + | gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no | ||
| + | SASA_score_secondary no | ||
| + | amber_score_secondary no | ||
| + | minimize_ligand no | ||
| + | atom_model all | ||
| + | vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn | ||
| + | flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn | ||
| + | flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl | ||
| + | ligand_outfile_prefix fps.min.output | ||
| + | write_footprints yes | ||
| + | write_hbonds yes | ||
| + | write_orientations no | ||
| + | num_scored_conformers 1 | ||
| + | rank_ligands no</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This should generate two output files: fps.min.output_hbond_scored.txt and fps.min.output_footprint_scored.txt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The latter can be visualized (in this case for 50 residues) using a python script which we can copy from the class directory: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre>cp /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/plot_footprint_single_magnitude.py ./ | ||
| + | python plot_footprint_single_magnitude.py fps.min.output_footprint_scored.txt 50</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:2p16_footprint.jpg]] | ||
== '''DOCKING''' == | == '''DOCKING''' == | ||
| Line 393: | Line 473: | ||
internal_energy_rep_exp 12 | internal_energy_rep_exp 12 | ||
internal_energy_cutoff 100.0 | internal_energy_cutoff 100.0 | ||
| − | ligand_atom_file 2p16. | + | ligand_atom_file 2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2 |
limit_max_ligands no | limit_max_ligands no | ||
skip_molecule no | skip_molecule no | ||
| Line 399: | Line 479: | ||
calculate_rmsd yes | calculate_rmsd yes | ||
use_rmsd_reference_mol yes | use_rmsd_reference_mol yes | ||
| − | rmsd_reference_filename 2p16. | + | rmsd_reference_filename 2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2 |
use_database_filter no | use_database_filter no | ||
orient_ligand no | orient_ligand no | ||
| Line 588: | Line 668: | ||
By looking at the comparison (green is the flex output), you can see that the pose reproduction went successfully. The output file showed the RMSD of 0.92 Å, which also indicates a success. This structure was found in the first in scored.mol2 showing that this pose was in fact the best pose after rotational bond and orientation searching. | By looking at the comparison (green is the flex output), you can see that the pose reproduction went successfully. The output file showed the RMSD of 0.92 Å, which also indicates a success. This structure was found in the first in scored.mol2 showing that this pose was in fact the best pose after rotational bond and orientation searching. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == ''' Virtual Screening ''' == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Virtual screening is a computational method of docking and ranking potential small molecule drug candidates. Leveraging the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the target receptor, virtual screening involves the systematic evaluation of a large library of small molecules by simulating their interactions with the target. By employing van der Waals, electrostatic, and interal energy scoring functions, virtual screening provides a way to rank and evaluate potential small molecule ligands. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For this tutorial, you will be using the VS_library_5K.mol2, located in /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/ and copied to our virtual screening directory. You can create a virtual screening directory (and then go into it) if you haven’t already: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | mkdir 005.virtual_screen | ||
| + | cd 005.virtual_screen | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | After that, create a new input file, vs.in: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | search_type flex | ||
| + | write_fragment_libraries no | ||
| + | user_specified_anchor no | ||
| + | limit_max_anchors no | ||
| + | min_anchor_size 5 | ||
| + | pruning_use_clustering yes | ||
| + | pruning_max_orients 1000 | ||
| + | pruning_clustering_cutoff 100 | ||
| + | pruning_conformer_score_cutoff 100.0 | ||
| + | pruning_conformer_score_scaling_factor 1.0 | ||
| + | use_clash_overlap no | ||
| + | write_growth_tree no | ||
| + | use_internal_energy yes | ||
| + | internal_energy_rep_exp 9 | ||
| + | internal_energy_cutoff 100.0 | ||
| + | ligand_atom_file VS_library_5K.mol2 | ||
| + | limit_max_ligands no | ||
| + | skip_molecule no | ||
| + | read_mol_solvation no | ||
| + | calculate_rmsd no | ||
| + | use_database_filter no | ||
| + | orient_ligand yes | ||
| + | automated_matching yes | ||
| + | receptor_site_file ../002.surface_spheres/selected_spheres.sph | ||
| + | max_orientations 1000 | ||
| + | critical_points no | ||
| + | chemical_matching no | ||
| + | use_ligand_spheres no | ||
| + | bump_filter no | ||
| + | score_molecules yes | ||
| + | contact_score_primary no | ||
| + | contact_score_secondary no | ||
| + | grid_score_primary yes | ||
| + | grid_score_secondary no | ||
| + | grid_score_rep_rad_scale 1 | ||
| + | grid_score_vdw_scale 1 | ||
| + | grid_score_es_scale 1 | ||
| + | grid_score_grid_prefix ../003.gridbox/grid | ||
| + | multigrid_score_secondary no | ||
| + | dock3.5_score_secondary no | ||
| + | continuous_score_secondary no | ||
| + | footprint_similarity_score_secondary no | ||
| + | pharmacophore_score_secondary no | ||
| + | descriptor_score_secondary no | ||
| + | gbsa_zou_score_secondary no | ||
| + | gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no | ||
| + | SASA_score_secondary no | ||
| + | amber_score_secondary no | ||
| + | minimize_ligand yes | ||
| + | minimize_anchor yes | ||
| + | minimize_flexible_growth yes | ||
| + | use_advanced_simplex_parameters no | ||
| + | simplex_max_cycles 1 | ||
| + | simplex_score_converge 0.1 | ||
| + | simplex_cycle_converge 1.0 | ||
| + | simplex_trans_step 1.0 | ||
| + | simplex_rot_step 0.1 | ||
| + | simplex_tors_step 10.0 | ||
| + | simplex_anchor_max_iterations 500 | ||
| + | simplex_grow_max_iterations 500 | ||
| + | simplex_grow_tors_premin_iterations 0 | ||
| + | simplex_random_seed 0 | ||
| + | simplex_restraint_min no | ||
| + | atom_model all | ||
| + | vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn | ||
| + | flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn | ||
| + | flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl | ||
| + | ligand_outfile_prefix 2p16_virtual_5k.out | ||
| + | write_orientations no | ||
| + | num_scored_conformers 1 | ||
| + | rank_ligands no | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | To make sure the virtual screen finishes in a timely manner, you will be utilizing MPI parallelization, which will allow you to use multiple nodes simultaneously for more processing power. Create a new file, 2p16_VS_5K.slurm, to give SLURM instructions on carrying out the virtual screen. It should look something like this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #!/bin/sh | ||
| + | #SBATCH --partition=long-28core | ||
| + | #SBATCH --time=2-00:00:00 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --nodes=4 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --ntasks=112 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --job-name=2p16_5k_vs | ||
| + | #SBATCH --output=log_2p16_5k_vs.txt | ||
| + | |||
| + | echo "starting DOCK6.10 Simulation" | ||
| + | module load intel_stack | ||
| + | |||
| + | mpirun -v -np 112 /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/bin/dock6.mpi -i vs.in -o vs.out | ||
| + | echo "done" | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This might be a bit overkill, so you may want to reduce the number of nodes or use a queue with fewer cores. The "echo" lines are there to provide an idea of whether the job started/finished properly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To submit this job to the queue, run: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | sbatch 2p16_VS_5K.slurm | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Each core will produce its own .out output file, but the only one of importance will be vs.out. This file should be transferred over to your local computer for viewing within Chimera, along with 2p16_virtual_5k.out_scored.mol2, which will contain the positions of the highest-scored ligands. Shown below are the aforementioned results in Chimera, as well as the comparison of the currently best-scored ligand and the original ligand: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:2P16_vsresult_original_withRec.png|thumb|center|500px|The original ligand (blue) compared to the best-scored ligand result from virtual screening (orange).]] [[File:2P16_VS_original_lig_structure.png|thumb|center|500px|Structural comparison between the original ligand (blue) and the best-scored ligand from virtual screening (orange) Note the various differences in ring structures between both structures.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == ''' Cartesian Minimization ''' == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Following the completion of the virtual screen, Cartesian minimization plays a pivotal role in refining the ligand-receptor complexes to obtain more accurate predictions of binding affinities. This process involves rigid docking of the ligands within the binding site to minimize the potential energy of the system. To start, we must create the proper directory and enter into it: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | mkdir 006.cartesian_min | ||
| + | cd 006.cartesian_min | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We will need to make a new input file for Cartesian minimization, min_scored.in: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | conformer_search_type rigid | ||
| + | use_internal_energy yes | ||
| + | internal_energy_rep_exp 12 | ||
| + | internal_energy_cutoff 100 | ||
| + | ligand_atom_file ../005.virtual_screen/2p16_virtual_5k.out_scored.mol2 | ||
| + | limit_max_ligands no | ||
| + | skip_molecule no | ||
| + | read_mol_solvation no | ||
| + | calculate_rmsd no | ||
| + | use_database_filter no | ||
| + | orient_ligand no | ||
| + | bump_filter no | ||
| + | score_molecules yes | ||
| + | vcontact_score_primary no | ||
| + | contact_score_secondary no | ||
| + | grid_score_primary no | ||
| + | grid_score_secondary no | ||
| + | multigrid_score_primary no | ||
| + | multigrid_score_secondary no | ||
| + | dock3.5_score_primary no | ||
| + | dock3.5_score_secondary no | ||
| + | continuous_score_primary yes | ||
| + | continuous_score_secondary no | ||
| + | cont_score_rec_filename ../001.files/2p16_rec_withH.mol2 | ||
| + | cont_score_att_exp 6 | ||
| + | cont_score_rep_exp 12 | ||
| + | cont_score_rep_rad_scale 1 | ||
| + | cont_score_use_dist_dep_dielectric yes | ||
| + | cont_score_dielectric 4.0 | ||
| + | cont_score_vdw_scale 1.0 | ||
| + | cont_score_es_scale 1.0 | ||
| + | footprint_similarity_score_secondary no | ||
| + | pharmacophore_score_secondary no | ||
| + | descriptor_score_secondary no | ||
| + | gbsa_zou_score_secondary no | ||
| + | gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no | ||
| + | SASA_score_secondary no | ||
| + | amber_score_secondary no | ||
| + | minimize_ligand yes | ||
| + | simplex_max_iterations 1000 | ||
| + | simplex_tors_premin_iterations 0 | ||
| + | simplex_max_cycles 1.0 | ||
| + | simplex_score_converge 0.1 | ||
| + | simplex_cycle_converge 1.0 | ||
| + | simplex_trans_step 1.0 | ||
| + | simplex_rot_step 0.1 | ||
| + | simplex_tors_step 10.0 | ||
| + | simplex_random_seed 0 | ||
| + | simplex_restraint_min no | ||
| + | atom_model all | ||
| + | vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn | ||
| + | flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn | ||
| + | flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl | ||
| + | ligand_outfile_prefix 2p16_vsc_cart_min | ||
| + | write_orientations no | ||
| + | num_scored_conformers 1 | ||
| + | rank_ligands no | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similar to virtual screening, you will need to run this on a Seawulf queue and utilize MPI. Create a slurm input file, cart_min.slurm, and add the following: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #!/bin/bash | ||
| + | #SBATCH --time=48:00:00 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --nodes=2 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --ntasks=28 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --job-name=2p16_VS_CM | ||
| + | #SBATCH --output=log_2p16_VS_CM.txt | ||
| + | #SBATCH -p long-28core | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd $SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR | ||
| + | echo “Starting Cartesian minimization!” | ||
| + | mpirun -np 56 /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/bin/dock6.mpi -i min_scored.in -o min_scored.out | ||
| + | echo “Done!” | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | When you are done with the previous instructions, you can submit the job: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | sbatch cart_min.slurm | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We used fewer nodes for this job compared to the virtual screen, but remember to change queue, number of cores, and number of nodes based on what works best: too many nodes or submitting to a popular queue may incur a significant wait time before the job starts. Too few cores or nodes and you may be waiting quite a while for the job to finish. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once finished, you can export 2p16_vsc_cart_min_scored.mol2 and min_scored.out to view the results. As you can see, the best grid-scored VS ligand may now be docked in a different position compared to the virtual screen results: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Ligand_structure_cartmin_vs1.png|thumb|center|500px|The previously shown ligand shown before Cartesian minimization (orange) and after (pink).]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == ''' Rescoring ''' == | ||
| + | |||
| + | After Cartesian minimization, our virtually screened ligands and their conformations should now be rescored. The various conformations and ligands can be scored (and eventually sorted) by other scoring functions, such as pharmacophore score, footprint similarity score, Hungarian score, etc. To start the final step of virtual screening, you will need to create a directory for rescoring: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | mkdir 007.rescore | ||
| + | cd 007.rescore | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | As you can guess, we then need to create an input file: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | vi rescore.in | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Into this file, paste the following: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | conformer_search_type rigid | ||
| + | use_internal_energy yes | ||
| + | internal_energy_rep_exp 12 | ||
| + | internal_energy_cutoff 100 | ||
| + | ligand_atom_file ../007.cartesianmin/2p16_vsc_min_scored.mol2 | ||
| + | limit_max_ligands no | ||
| + | skip_molecule no | ||
| + | read_mol_solvation no | ||
| + | calculate_rmsd no | ||
| + | use_database_filter no | ||
| + | orient_ligand no | ||
| + | bump_filter no | ||
| + | score_molecules yes | ||
| + | contact_score_primary no | ||
| + | contact_score_secondary no | ||
| + | grid_score_primary no | ||
| + | grid_score_secondary no | ||
| + | multigrid_score_primary no | ||
| + | multigrid_score_secondary no | ||
| + | dock3.5_score_primary no | ||
| + | dock3.5_score_secondary no | ||
| + | continuous_score_primary no | ||
| + | continuous_score_secondary no | ||
| + | footprint_similarity_score_primary no | ||
| + | footprint_similarity_score_secondary no | ||
| + | pharmacophore_score_primary no | ||
| + | pharmacophore_score_secondary no | ||
| + | descriptor_score_primary yes | ||
| + | descriptor_score_secondary no | ||
| + | descriptor_use_grid_score no | ||
| + | descriptor_use_multigrid_score no | ||
| + | descriptor_use_continuous_score no | ||
| + | descriptor_use_footprint_similarity yes | ||
| + | descriptor_use_pharmacophore_score yes | ||
| + | descriptor_use_hungarian yes | ||
| + | descriptor_use_volume_overlap yes | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_use_footprint_reference_mol2 yes | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_footprint_reference_mol2_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_foot_compare_type Euclidean | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_normalize_foot no | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_foot_comp_all_residue yes | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_receptor_filename ../001.files/2p16_rec_withH.mol2 | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_vdw_att_exp 6 | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_vdw_rep_exp 12 | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_vdw_rep_rad_scale 1 | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_use_distance_dependent_dielectric yes | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_dielectric 4.0 | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_vdw_fp_scale 1 | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_es_fp_scale 1 | ||
| + | descriptor_fps_score_hb_fp_scale 0 | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_use_ref_mol2 yes | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_ref_mol2_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_write_reference_pharmacophore_mol2 no | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_write_reference_pharmacophore_txt no | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_write_candidate_pharmacophore no | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_write_matched_pharmacophore no | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_compare_type overlap | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_full_match yes | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_match_rate_weight 5.0 | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_match_dist_cutoff 1.0 | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_match_proj_cutoff .7071 | ||
| + | descriptor_fms_score_max_score 20 | ||
| + | descriptor_fingerprint_ref_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 | ||
| + | descriptor_hms_score_ref_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 | ||
| + | descriptor_hms_score_matching_coeff -5 | ||
| + | descriptor_hms_score_rmsd_coeff 1 | ||
| + | descriptor_volume_score_reference_mol2_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 | ||
| + | descriptor_volume_score_overlap_compute_method analytical | ||
| + | descriptor_weight_fps_score 1 | ||
| + | descriptor_weight_pharmacophore_score 1 | ||
| + | descriptor_weight_fingerprint_tanimoto -1 | ||
| + | descriptor_weight_hms_score 1 | ||
| + | descriptor_weight_volume_overlap_score -1 | ||
| + | gbsa_zou_score_secondary no | ||
| + | gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no | ||
| + | SASA_score_secondary no | ||
| + | amber_score_secondary no | ||
| + | minimize_ligand no | ||
| + | atom_model all | ||
| + | vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn | ||
| + | flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn | ||
| + | flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl | ||
| + | chem_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/chem.defn | ||
| + | pharmacophore_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/ph4.defn | ||
| + | ligand_outfile_prefix 2p16_rescored.out | ||
| + | write_footprints yes | ||
| + | write_hbonds yes | ||
| + | write_orientations no | ||
| + | num_scored_conformers 1 | ||
| + | rank_ligands no | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is going to be a larger job, so you should run this parallelized on Seawulf: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | vi rescore.sh | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | Here’s another example slurm batch file that should cover the running of your job: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #!/bin/bash | ||
| + | #SBATCH --time=4:00:00 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --nodes=2 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --ntasks=28 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --job-name=2p16_VS_rescore | ||
| + | #SBATCH --output=log_2p16_rescore.txt | ||
| + | #SBATCH -p short-28core | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd $SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR | ||
| + | mpirun -np 56 /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/bin/dock6.mpi -i rescore.in -o rescore.out | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once saved, submit it to Slurm via: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | sbatch rescore.sh | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Each core will produce its own .out output file, but the only rescore.out file of importance will be the unnumbered rescore.out. However, the “xxxx_rescored.out_scored.mol2” will contain all of the scored ligands, along with all of their descriptor scores. There will also be “xxx_rescored.out_descriptor_scored.txt” files that provide more details about the ligands, including potential hydrogen bonding interactions and footprints. These files should be transferred over to your local computer for viewing within Chimera via ViewDock, along with “xxxx_rescored.out_scored.mol2”. | ||
Latest revision as of 16:20, 12 February 2024
Contents
Introduction
Docking is a molecular modeling program useful for drug discovery. It computes optimal binding conformations and affinities of a small molecule to its target protein using sampling and scoring methods respectively. It enables the discovery of new low-energy ligand binding modes to the active site of a protein, which can help optimize existing drugs or discover new candidates.
DOCK6
DOCK6 was initially developed at UCSF and now is maintained by several groups across three universities. In addition to other features, it introduces new sampling methods such as fixed anchor, de novo design, and genetic algorithms as improvements over traditional rigid docking methods.
In this tutorial we will be exploring the following functions:
- Docking- rigid, flexible, and fixed anchor
- Virtual Screening- docking large libraries of compounds against a protein to generate drug lead
- Cartesian Minimization- energy minimization of docked molecules in the active site
2P16 System
2p16 refers to the pdb code for the crystal structure of Factor Xa in complex with its inhibitor Apixaban.
Factor Xa plays a key role in the formation of blood clots and is therefore a drug target for anticoagulants.
The drug Apixaban is a second-generation therapy developed by Bristol Myers Squibb- it has fewer drug interactions than the more traditional Heparin and Warfarin, and therefore can be used in patients with additional complications. A docking study of this system may elucide the mechanism of this increased specificity and help design the next generation of specific inhibitors.
Directory Structure
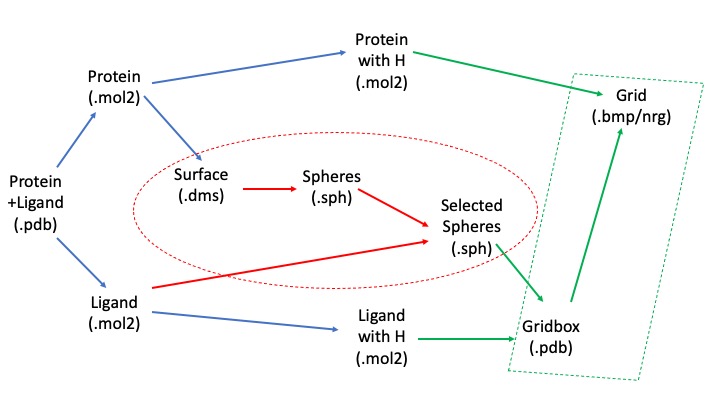
In order to understand the necessary directories it's important to understand the workflow of this project:
We will begin with the pdb file, clean up and separate out the protein and ligand, and then use the unprotonated forms to calculate spheres representing the molecular surface. We will then use our protonated form along with the spheres to calculate the scoring grid. The blue arrows represent transformations we can make using Chimera, the red ones using the SPHGEN and sphere_selector commands, and the green ones using showbox and grid commands.
We will need directories for each step of this process- the sphere generation, grid generation, structure files, as well as for the docking, virtual screening, cartesian minimization, and rescoring after the initial preparatory phase. You can use the following commands to log into the cluster and the generate the relevant directories:
ssh username@login.seawulf.stonybrook.edu cd /gpfs/projects/AMS536/your_docking_tutorial_directory mkdir structures spheres gridbox dock virtual_screen virtual_screen_mpi cartesian_min rescore
Protein and Ligand Preparation
Download the 2p16.pdb file from the pdb website, save it in the structures directory, and visualize it using Chimera. You may do so using the command line:
cd structures wget https://files.rcsb.org/download/2P16.pdb chimera 2P16.pdb
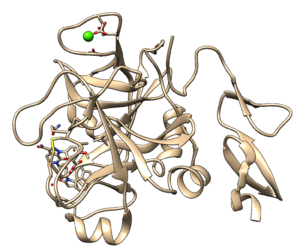
Make sure you read the associated paper to get an understanding protonation states, charges, and crystallization conditions. Identify the following components- protein, ligand, ions, and solvent.
We will be assuming biological pH and neglecting solvent and ion effects, so you can delete the ions, solvent, and protein chain that isn't involved in ligand binding using the following Chimera commands:
Select->Structure->ion Actions->Atoms/Bonds->delete Select->Structure->solvent Actions->Atoms/Bonds->delete Select->Chain->L Actions->Atoms/Bonds->delete
Save the file as 2p16_cleaned.pdb
Protein Preparation
To prepare the protein file delete the ligand:
Select->Structure->ligand Actions->Atoms/Bonds->delete
Save the file as 2p16_noh_protein.mol2 using File-> Save Mol2
To add hydrogens and charge, you may use the Dockprep function in Chimera through Tools->Surface/Binding Analysis->Dock Prep. Uncheck delete solvent in the first window, as we have done this manually, and press ok until you reach the "Assign Charges" window. Ensure that AMBER ff14SB is selected in this window and AM1-BCC in the following "Specify Net Charges" window. Save the file as 2p16_dockprep_protein.mol2
Ligand Preparation
To prepare the ligand file load 2p16_cleaned.pdb and delete the protein:
Select->Chain->A Actions->Atoms/Bonds->delete
Save the file as 2p16_noh_ligand.mol2 using File-> Save Mol2
Add hydrogens and charge using Dockprep. Save the file as 2p16_dockprep_ligand.mol2
Surface Spheres
The remainder of this tutorial will rely on commands from the DOCK6 program. Please ensure that you have DOCK6.10 installed and accessible in your path, which you can check using the commands:
which dock echo $PATH
If not, you may want to check your ~/.bashrc file and add the following lines if needed:
export DOCKHOME="/gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10" PATH=$DOCKHOME/bin\:$PATH export PATH=$DOCKHOME/bin\:$PATH
Save the file and activate it using:
source ~/.bashrc
DMS Preparation
To prepare the DMS file open 2p16_noh_protein.mol2 in Chimera and do the following:
Action->Surface->Show Tools->Structure Editing->Write DMS
Save the file as 2p16_noh_protein.dms
Sphere Generation
Transfer all the files generated so far to the structures directory in your Seawulf docking directory using:
scp 2p16* username@login.seawulf.stonybrook.edu:/gpfs/projects/AMS536/your_docking_tutorial_directory/structures
Move to the spheres directory and open an input file for the sphgen command:
cd spheres vim INSPH
Type in the following and save the file:
../structures/2p16_noh_protein.dms #input file R #spheres to be generated outside the receptor surface X #all surface points to be used 0.0 #surface clashes 4.0. #max sphere radius 1.4. #min sphere radius 2p16_protein.sph #output file
Run sphgen using:
sphgen -i INSPH -o OUTSPH
Open your output file 2p16_protein.sph along with your 2016_noh_protein.mol2 file to check if everything looks ok.
Sphere Selection
We now need to narrow down the generated spheres to only those near the binding pocket.
The following command will select those within 10 angstroms of the ligand and save them to selected_spheres.sph:
sphere_selector 2p16_protein.sph ../structures/2p16_noh_ligand.mol2 10.0
Grid Box
We will now use the selected spheres to generate a grid within which we will score the sampled molecular conformations.
Box Generation
Move to the gridbox directory and open up an input file titled showbox.in. Type in the following text:
Y #Yes to making a box 8.0 #Angstroms between box boundary and any sphere ../spheres/selected_spheres.sph #Input file 1 #Number of clusters of spheres to use 2p16.box.pdb #Output file
Generate the box using the following command:
showbox < showbox.in
Grid Generation
Open up an input file titled grid.in and type in the following:
allow_non_integral_charges no compute_grids yes grid_spacing 0.4 output_molecule no contact_score no energy_score yes energy_cutoff_distance 9999 atom_model a attractive_exponent 6 repulsive_exponent 9 distance_dielectric yes dielectric_factor 4 bump_filter yes bump_overlap 0.75 receptor_file ../structures/2p16_dockprep_protein.mol2 box_file 2p16.box.pdb vdw_definition_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn score_grid_prefix grid
Generate the grid using the following command:
grid -i grid.in -o grid.out
This should create a grid.out, grid.nrg, and grid.bmp file. Check the grid.out file to see if your residue charges and total charge match the original protein mol2 file. If not, go back and check if you made any mistakes in earlier steps.
Ligand Minimization
Before running DOCK we need to ensure our ligand is energy minimized to prevent any steric clashes.
Switch to the dock directory and open up an input file called min.in and type in the following:
conformer_search_type rigid use_internal_energy yes internal_energy_rep_exp 12 internal_energy_cutoff 100.0 ligand_atom_file ../structures/2p16_dockprep_ligand.mol2 limit_max_ligands no skip_molecule no read_mol_solvation no calculate_rmsd yes use_rmsd_reference_mol ../structures/2p16_dockprep_ligand.mol2 use_database_filter no orient_ligand no bump_filter no score_molecules yes contact_score_primary no contact_score_secondary no grid_score_primary yes grid_score_secondary no grid_score_rep_rad_scale 1 grid_score_vdw_scale 1 grid_score_es_scale 1 grid_score_grid_prefix ../gridbox/grid multigrid_score_secondary no dock3.5_score_secondary no continuous_score_secondary no footprint_similarity_score_secondary no pharmacophore_score_secondary no descriptor_score_secondary no gbsa_zou_score_secondary no gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no SASA_score_secondary no amber_score_secondary no minimize_ligand yes simplex_max_iterations 1000 simplex_tors_premin_iterations 0 simplex_max_cycles 1 simplex_score_converge 0.1 simplex_cycle_converge 1.0 simplex_trans_step 1.0 simplex_rot_step 0.1 simplex_tors_step 10.0 simplex_random_seed 0 simplex_restraint_min yes simplex_coefficient_restraint 10.0 atom_model all vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl ligand_outfile_prefix 2p16_ligand.min write_orientations no num_scored_conformers 1 rank_ligands no
Run the minimization using:
dock6 -i min.in -o min.out
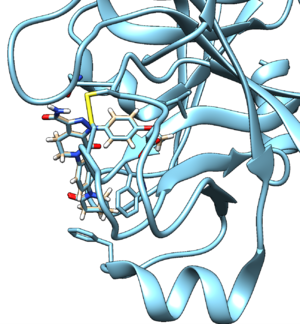
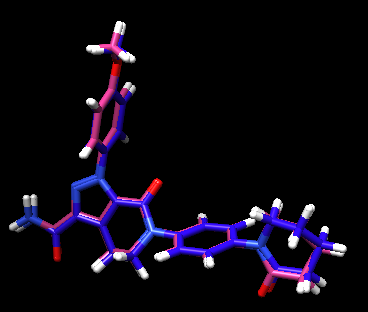
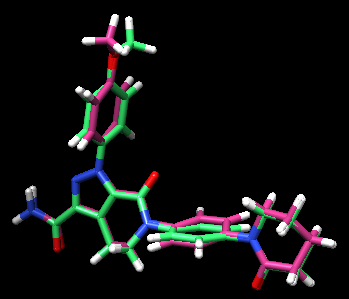
This should save a new file called 2p16_ligand.min_scored.mol2. Open it up in Chimera along with the protein and ligand mol2 files for comparison.
You can also view the RMSD values in the header of the file using:
head 2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2
Footprint Analysis
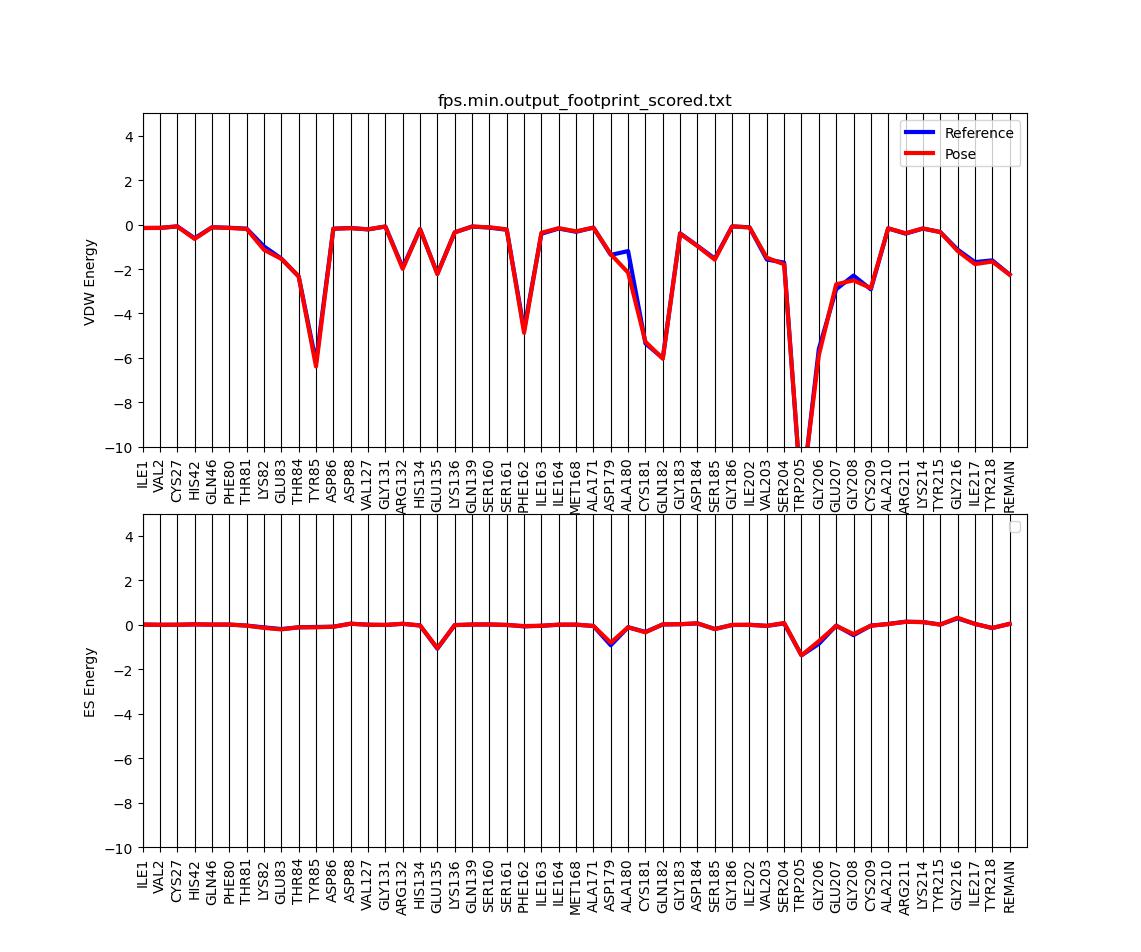
We can use footprinting to visualize the protein-ligand interaction energies on a per-residue basis.
In the same dock directory open up an input file called footprint.in and type in the following:
conformer_search_type rigid use_internal_energy no ligand_atom_file 2p16_ligand.min_scored.mol2 limit_max_ligands no skip_molecule no read_mol_solvation no calculate_rmsd no use_database_filter no orient_ligand no bump_filter no score_molecules yes contact_score_primary no contact_score_secondary no grid_score_primary no grid_score_secondary no multigrid_score_primary no multigrid_score_secondary no dock3.5_score_primary no dock3.5_score_secondary no continuous_score_primary no continuous_score_secondary no footprint_similarity_score_primary yes footprint_similarity_score_secondary no fps_score_use_footprint_reference_mol2 yes fps_score_footprint_reference_mol2_filename ../structures/2p16_dockprep_ligand.mol2 fps_score_foot_compare_type Euclidean fps_score_normalize_foot no fps_score_foot_comp_all_residue yes fps_score_receptor_filename ../structures/2p16_dockprep_protein.mol2 fps_score_vdw_att_exp 6 fps_score_vdw_rep_exp 9 fps_score_vdw_rep_rad_scale 1 fps_score_use_distance_dependent_dielectric yes fps_score_dielectric 4.0 fps_score_vdw_fp_scale 1 fps_score_es_fp_scale 1 fps_score_hb_fp_scale 0 pharmacophore_score_secondary no descriptor_score_secondary no gbsa_zou_score_secondary no gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no SASA_score_secondary no amber_score_secondary no minimize_ligand no atom_model all vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl ligand_outfile_prefix fps.min.output write_footprints yes write_hbonds yes write_orientations no num_scored_conformers 1 rank_ligands no
This should generate two output files: fps.min.output_hbond_scored.txt and fps.min.output_footprint_scored.txt.
The latter can be visualized (in this case for 50 residues) using a python script which we can copy from the class directory:
cp /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/plot_footprint_single_magnitude.py ./ python plot_footprint_single_magnitude.py fps.min.output_footprint_scored.txt 50
DOCKING
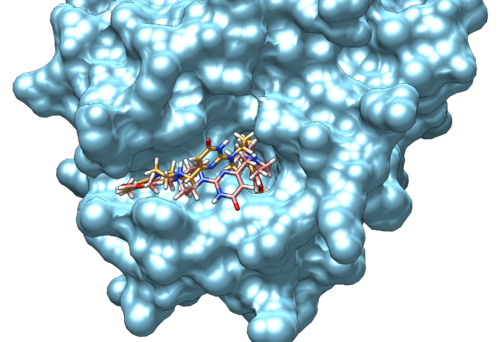
The goal of docking in this tutorial is to reproduce the crystal structure from x-ray diffraction. This is called “pose reproduction”; this can be used to validate the docking software and parameters of use within the software. If the pose reproduction is not successful, it might be possible that: 1.the parameters to dock the ligand needs to be changed, 2.preparation of ligand or receptor went wrong, 3.the system itself is not suitable to reproduce in the software. Having a preliminary docking pose before getting into virtual screening–a procedure docking thousands of molecules–would be helpful to validate the results you will get in the future. In DOCK6 (at the point of 2020), the docking is successful if the RMSD of the docked pose is within 2.0Å from the crystal pose. In this section, we will be working on (i)rigid docking, (ii)flexible docking, (iii)fixed anchor docking.
Rigid Docking
Rigid docking does not conduct pose searching with dihedral rotations or bond length perturbations. It takes 3 translational and 3 rotational degrees of freedom to do its pose searching. Therefore, rigid docking is less computationally expensive compared to flex docking. Since we already have the crystal structure of the ligand bound at the active site, it is expected to have a good reproduction using rigid docking.
The first step is to create an input file by rigid.in
Insert the following into that file:
conformer_search_type rigid use_internal_energy yes internal_energy_rep_exp 12 internal_energy_cutoff 100 ligand_atom_file 2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2 limit_max_ligands no skip_molecule no read_mol_solvation no calculate_rmsd yes use_rmsd_reference_mol yes rmsd_reference_filename 2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2 use_database_filter no orient_ligand yes automated_matching yes receptor_site_file selected_spheres.sph max_orientations 2000 critical_points no chemical_matching no use_ligand_spheres no bump_filter no score_molecules yes contact_score_primary no contact_score_secondary no grid_score_primary yes grid_score_secondary no grid_score_rep_rad_scale 1 grid_score_vdw_scale 1 grid_score_es_scale 1 grid_score_grid_prefix grid multigrid_score_secondary no dock3.5_score_secondary no continuous_score_secondary no footprint_similarity_score_secondary no pharmacophore_score_secondary no descriptor_score_secondary no gbsa_zou_score_secondary no gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no SASA_score_secondary no amber_score_secondary no minimize_ligand yes simplex_max_iterations 1000 simplex_tors_premin_iterations 0 simplex_max_cycles 1 simplex_score_converge 0.1 simplex_cycle_converge 1.0 simplex_trans_step 1.0 simplex_rot_step 0.1 simplex_tors_step 10.0 simplex_random_seed 0 simplex_restraint_min no atom_model all vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl ligand_outfile_prefix rigid.out write_orientations no num_scored_conformers 1 rank_ligands no
Make sure to (i)have all the files you need (selected_spheres.sph and 2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2) and (ii)inputs are correct.
Run the input file with the following command:
dock6 -i rigid.in -o rigid.out
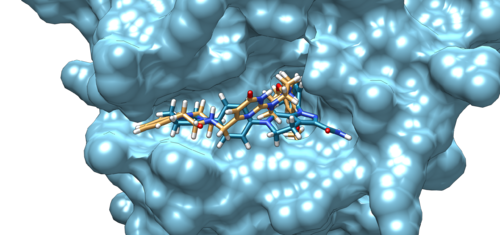
After the job is complete, you should see a file named “rigid.out_scored.mol2”. This is the output that shows the docked poses (if you rank it, it will show from the highest to lowest docking score). If you open the file, in the first part, you will see general information about the docked pose including the grid scores. Make sure that the output file is not empty.
The pose can be visualized using Chimera.
After you load the protein you prepared (simply open the file), you can go to:
Tools -> Surface/Binding Analysis -> ViewDock -> *choose the file* -> Dock4,5, or 6.
Along with the visualized pose, you will see a small window popping out with the quantitative information as you saw in the first part of the output file.
Since we took a crystal structure of the ligand, minimized, and rigidly docked into the same protein, it is expected that the produced pose is well-reproduced.
If you want to check the reproducibility, you could check out the RMSD (root-mean-square-deviation) values for the pose.
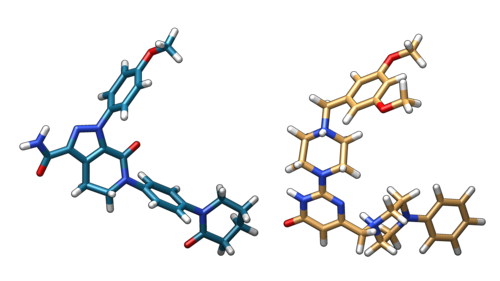
The crystal reference ligand is colored in pink
From the result pose, you can see that the pose reproduction was not successful. From the scored.mol2 file, the RMSD was indicated to be 7.4 Å, which is above 2.0 Å cutoff for a successful pose reproduction. Although this was an unexpected results from the initial assumption, but we can try using two other methods: flex and fixed anchor docking.
Fixed Anchor Docking
As it is said “fixed anchor” docking, this is a docking method that docks while maintaining the orientation of the initially placed structure. For this reason, “comformer_search_type” is flexible, while “write orientation” is turned off. This allows more flexibility in its conformational change compared to rigid docking methods while maintaining the general placement. You can also pick specific fragments within the molecules to be the anchor.
Not to mess up the outputs with other types of docking methods, make a new folder by
mkdir anchor_dock
In this directory, create an input file:
vi fixed.in
Insert the following:
conformer_search_type flex write_fragment_libraries no user_specified_anchor no limit_max_anchors no min_anchor_size 5 pruning_use_clustering yes pruning_max_orients 10000 pruning_clustering_cutoff 100 pruning_conformer_score_cutoff 100.0 pruning_conformer_score_scaling_factor 1.0 use_clash_overlap no write_growth_tree no use_internal_energy yes internal_energy_rep_exp 12 internal_energy_cutoff 100.0 ligand_atom_file 2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2 limit_max_ligands no skip_molecule no read_mol_solvation no calculate_rmsd yes use_rmsd_reference_mol yes rmsd_reference_filename 2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2 use_database_filter no orient_ligand no bump_filter no score_molecules yes contact_score_primary no contact_score_secondary no grid_score_primary yes grid_score_secondary no grid_score_rep_rad_scale 1 grid_score_vdw_scale 1 grid_score_es_scale 1 grid_score_grid_prefix grid multigrid_score_secondary no dock3.5_score_secondary no continuous_score_secondary no footprint_similarity_score_secondary no pharmacophore_score_secondary no descriptor_score_secondary no gbsa_zou_score_secondary no gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no SASA_score_secondary no amber_score_secondary no minimize_ligand yes minimize_anchor yes minimize_flexible_growth yes use_advanced_simplex_parameters no simplex_max_cycles 1 simplex_score_converge 0.1 simplex_cycle_converge 1 simplex_trans_step 1 simplex_rot_step 0.1 simplex_tors_step 10 simplex_anchor_max_iterations 500 simplex_grow_max_iterations 500 simplex_grow_tors_premin_iterations 0 simplex_random_seed 0 simplex_restraint_min no atom_model all vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl ligand_outfile_prefix 2P16_fixed write_orientations no num_scored_conformers 1 rank_ligands no
Start the docking by:
dock6 -i fixed.in -o fixed.out
The resulting docked pose:
The RMSD in this result was 0.22 Å, which is well within 2.0 Å (success cutoff). From the rigid docking result, we could see that the orientation of the entire molecule was flipped from the minimized crystal structure. By having a part of the molecule anchored, it seemed that the big rotation of this molecule did not occur. For a case of new compounds, ones that do not have a crystal structures, this method allows more chemical exploration.
Flex Docking
Finally, flex docking is a docking method that allows flexibility in the rotatable bonds in the ligand and orientation of the compound. This method has the largest exploration of the pose for the ligand, although the calculation time takes the longest. To speed up the calculation time, it is necessary to use cpus provided in seawulf. To use the cpus, we need to submit our run to the queue.
Create a directory:
mkdir flex_dock
First, start with creating an input file, flex.in.
conformer_search_type flex write_fragment_libraries no user_specified_anchor no limit_max_anchors no min_anchor_size 5 pruning_use_clustering yes pruning_max_orients 5000 pruning_clustering_cutoff 2500 pruning_conformer_score_cutoff 100.0 pruning_conformer_score_scaling_factor 1.0 use_clash_overlap no write_growth_tree no use_internal_energy yes internal_energy_rep_exp 12 internal_energy_cutoff 100.0 ligand_atom_file ../Rigid_dock/2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2 limit_max_ligands no skip_molecule no read_mol_solvation no calculate_rmsd yes use_rmsd_reference_mol yes rmsd_reference_filename ../Rigid_dock/2p16.ligand.min_scored.mol2 use_database_filter no orient_ligand yes automated_matching yes receptor_site_file ../Rigid_dock/selected_spheres.sph max_orientations 1000 critical_points no chemical_matching no use_ligand_spheres no bump_filter no score_molecules yes contact_score_primary no contact_score_secondary no grid_score_primary yes grid_score_secondary no grid_score_rep_rad_scale 1 grid_score_vdw_scale 1 grid_score_es_scale 1 grid_score_grid_prefix ../Rigid_dock/grid multigrid_score_secondary no dock3.5_score_secondary no continuous_score_secondary no footprint_similarity_score_secondary no pharmacophore_score_secondary no descriptor_score_secondary no gbsa_zou_score_secondary no gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no SASA_score_secondary no amber_score_secondary no minimize_ligand yes minimize_anchor yes minimize_flexible_growth yes use_advanced_simplex_parameters no simplex_max_cycles 1 simplex_score_converge 0.1 simplex_cycle_converge 1.0 simplex_trans_step 1.0 simplex_rot_step 0.1 simplex_tors_step 10.0 simplex_anchor_max_iterations 500 simplex_grow_max_iterations 500 simplex_grow_tors_premin_iterations 0 simplex_random_seed 0 simplex_restraint_min no atom_model all vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl ligand_outfile_prefix flex.out write_orientations yes num_scored_conformers 10 write_conformations yes cluster_conformations yes cluster_rmsd_threshold 2.0 rank_ligands no
Now that we have our .in file, we need to make a slurm script to run it. To make a script, first run the following:
vi flex.sh
Inside of this file, copy-paste the following:
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --time=10:00:00 #SBATCH --nodes=1 #SBATCH --ntasks=28 #SBATCH --job-name=2p16_flex_dock #SBATCH --output=2p16_flex_dock #SBATCH -p long-28core
dock6 -i flex.in -o 2p16_flex.out
You can submit the queue by
sbatch flex.sh
Once complete, you will see three .mol2 files: (1)flex.out_scored.mol2: best poses scored from the highest to lowest (2)flex.out_conformers.mol2: poses with all conformations of the ligand (3)flex.out_orients.mol2: poses with all orientations of the ligand
To check the best pose, check the flex.out_scored.mol2. You can open it on Chimera using viewdock. Compare with the crystal structure - is the pose with freedom of orientation and rotatable bonds matching with the binding pose in real life?
By looking at the comparison (green is the flex output), you can see that the pose reproduction went successfully. The output file showed the RMSD of 0.92 Å, which also indicates a success. This structure was found in the first in scored.mol2 showing that this pose was in fact the best pose after rotational bond and orientation searching.
Virtual Screening
Virtual screening is a computational method of docking and ranking potential small molecule drug candidates. Leveraging the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the target receptor, virtual screening involves the systematic evaluation of a large library of small molecules by simulating their interactions with the target. By employing van der Waals, electrostatic, and interal energy scoring functions, virtual screening provides a way to rank and evaluate potential small molecule ligands.
For this tutorial, you will be using the VS_library_5K.mol2, located in /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/ and copied to our virtual screening directory. You can create a virtual screening directory (and then go into it) if you haven’t already:
mkdir 005.virtual_screen cd 005.virtual_screen
After that, create a new input file, vs.in:
search_type flex write_fragment_libraries no user_specified_anchor no limit_max_anchors no min_anchor_size 5 pruning_use_clustering yes pruning_max_orients 1000 pruning_clustering_cutoff 100 pruning_conformer_score_cutoff 100.0 pruning_conformer_score_scaling_factor 1.0 use_clash_overlap no write_growth_tree no use_internal_energy yes internal_energy_rep_exp 9 internal_energy_cutoff 100.0 ligand_atom_file VS_library_5K.mol2 limit_max_ligands no skip_molecule no read_mol_solvation no calculate_rmsd no use_database_filter no orient_ligand yes automated_matching yes receptor_site_file ../002.surface_spheres/selected_spheres.sph max_orientations 1000 critical_points no chemical_matching no use_ligand_spheres no bump_filter no score_molecules yes contact_score_primary no contact_score_secondary no grid_score_primary yes grid_score_secondary no grid_score_rep_rad_scale 1 grid_score_vdw_scale 1 grid_score_es_scale 1 grid_score_grid_prefix ../003.gridbox/grid multigrid_score_secondary no dock3.5_score_secondary no continuous_score_secondary no footprint_similarity_score_secondary no pharmacophore_score_secondary no descriptor_score_secondary no gbsa_zou_score_secondary no gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no SASA_score_secondary no amber_score_secondary no minimize_ligand yes minimize_anchor yes minimize_flexible_growth yes use_advanced_simplex_parameters no simplex_max_cycles 1 simplex_score_converge 0.1 simplex_cycle_converge 1.0 simplex_trans_step 1.0 simplex_rot_step 0.1 simplex_tors_step 10.0 simplex_anchor_max_iterations 500 simplex_grow_max_iterations 500 simplex_grow_tors_premin_iterations 0 simplex_random_seed 0 simplex_restraint_min no atom_model all vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl ligand_outfile_prefix 2p16_virtual_5k.out write_orientations no num_scored_conformers 1 rank_ligands no
To make sure the virtual screen finishes in a timely manner, you will be utilizing MPI parallelization, which will allow you to use multiple nodes simultaneously for more processing power. Create a new file, 2p16_VS_5K.slurm, to give SLURM instructions on carrying out the virtual screen. It should look something like this:
#!/bin/sh #SBATCH --partition=long-28core #SBATCH --time=2-00:00:00 #SBATCH --nodes=4 #SBATCH --ntasks=112 #SBATCH --job-name=2p16_5k_vs #SBATCH --output=log_2p16_5k_vs.txt echo "starting DOCK6.10 Simulation" module load intel_stack mpirun -v -np 112 /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/bin/dock6.mpi -i vs.in -o vs.out echo "done"
This might be a bit overkill, so you may want to reduce the number of nodes or use a queue with fewer cores. The "echo" lines are there to provide an idea of whether the job started/finished properly.
To submit this job to the queue, run:
sbatch 2p16_VS_5K.slurm
Each core will produce its own .out output file, but the only one of importance will be vs.out. This file should be transferred over to your local computer for viewing within Chimera, along with 2p16_virtual_5k.out_scored.mol2, which will contain the positions of the highest-scored ligands. Shown below are the aforementioned results in Chimera, as well as the comparison of the currently best-scored ligand and the original ligand:
Cartesian Minimization
Following the completion of the virtual screen, Cartesian minimization plays a pivotal role in refining the ligand-receptor complexes to obtain more accurate predictions of binding affinities. This process involves rigid docking of the ligands within the binding site to minimize the potential energy of the system. To start, we must create the proper directory and enter into it:
mkdir 006.cartesian_min cd 006.cartesian_min
We will need to make a new input file for Cartesian minimization, min_scored.in:
conformer_search_type rigid use_internal_energy yes internal_energy_rep_exp 12 internal_energy_cutoff 100 ligand_atom_file ../005.virtual_screen/2p16_virtual_5k.out_scored.mol2 limit_max_ligands no skip_molecule no read_mol_solvation no calculate_rmsd no use_database_filter no orient_ligand no bump_filter no score_molecules yes vcontact_score_primary no contact_score_secondary no grid_score_primary no grid_score_secondary no multigrid_score_primary no multigrid_score_secondary no dock3.5_score_primary no dock3.5_score_secondary no continuous_score_primary yes continuous_score_secondary no cont_score_rec_filename ../001.files/2p16_rec_withH.mol2 cont_score_att_exp 6 cont_score_rep_exp 12 cont_score_rep_rad_scale 1 cont_score_use_dist_dep_dielectric yes cont_score_dielectric 4.0 cont_score_vdw_scale 1.0 cont_score_es_scale 1.0 footprint_similarity_score_secondary no pharmacophore_score_secondary no descriptor_score_secondary no gbsa_zou_score_secondary no gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no SASA_score_secondary no amber_score_secondary no minimize_ligand yes simplex_max_iterations 1000 simplex_tors_premin_iterations 0 simplex_max_cycles 1.0 simplex_score_converge 0.1 simplex_cycle_converge 1.0 simplex_trans_step 1.0 simplex_rot_step 0.1 simplex_tors_step 10.0 simplex_random_seed 0 simplex_restraint_min no atom_model all vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl ligand_outfile_prefix 2p16_vsc_cart_min write_orientations no num_scored_conformers 1 rank_ligands no
Similar to virtual screening, you will need to run this on a Seawulf queue and utilize MPI. Create a slurm input file, cart_min.slurm, and add the following:
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --time=48:00:00 #SBATCH --nodes=2 #SBATCH --ntasks=28 #SBATCH --job-name=2p16_VS_CM #SBATCH --output=log_2p16_VS_CM.txt #SBATCH -p long-28core cd $SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR echo “Starting Cartesian minimization!” mpirun -np 56 /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/bin/dock6.mpi -i min_scored.in -o min_scored.out echo “Done!”
When you are done with the previous instructions, you can submit the job:
sbatch cart_min.slurm
We used fewer nodes for this job compared to the virtual screen, but remember to change queue, number of cores, and number of nodes based on what works best: too many nodes or submitting to a popular queue may incur a significant wait time before the job starts. Too few cores or nodes and you may be waiting quite a while for the job to finish.
Once finished, you can export 2p16_vsc_cart_min_scored.mol2 and min_scored.out to view the results. As you can see, the best grid-scored VS ligand may now be docked in a different position compared to the virtual screen results:
Rescoring
After Cartesian minimization, our virtually screened ligands and their conformations should now be rescored. The various conformations and ligands can be scored (and eventually sorted) by other scoring functions, such as pharmacophore score, footprint similarity score, Hungarian score, etc. To start the final step of virtual screening, you will need to create a directory for rescoring:
mkdir 007.rescore cd 007.rescore
As you can guess, we then need to create an input file:
vi rescore.in
Into this file, paste the following:
conformer_search_type rigid use_internal_energy yes internal_energy_rep_exp 12 internal_energy_cutoff 100 ligand_atom_file ../007.cartesianmin/2p16_vsc_min_scored.mol2 limit_max_ligands no skip_molecule no read_mol_solvation no calculate_rmsd no use_database_filter no orient_ligand no bump_filter no score_molecules yes contact_score_primary no contact_score_secondary no grid_score_primary no grid_score_secondary no multigrid_score_primary no multigrid_score_secondary no dock3.5_score_primary no dock3.5_score_secondary no continuous_score_primary no continuous_score_secondary no footprint_similarity_score_primary no footprint_similarity_score_secondary no pharmacophore_score_primary no pharmacophore_score_secondary no descriptor_score_primary yes descriptor_score_secondary no descriptor_use_grid_score no descriptor_use_multigrid_score no descriptor_use_continuous_score no descriptor_use_footprint_similarity yes descriptor_use_pharmacophore_score yes descriptor_use_hungarian yes descriptor_use_volume_overlap yes descriptor_fps_score_use_footprint_reference_mol2 yes descriptor_fps_score_footprint_reference_mol2_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 descriptor_fps_score_foot_compare_type Euclidean descriptor_fps_score_normalize_foot no descriptor_fps_score_foot_comp_all_residue yes descriptor_fps_score_receptor_filename ../001.files/2p16_rec_withH.mol2 descriptor_fps_score_vdw_att_exp 6 descriptor_fps_score_vdw_rep_exp 12 descriptor_fps_score_vdw_rep_rad_scale 1 descriptor_fps_score_use_distance_dependent_dielectric yes descriptor_fps_score_dielectric 4.0 descriptor_fps_score_vdw_fp_scale 1 descriptor_fps_score_es_fp_scale 1 descriptor_fps_score_hb_fp_scale 0 descriptor_fms_score_use_ref_mol2 yes descriptor_fms_score_ref_mol2_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 descriptor_fms_score_write_reference_pharmacophore_mol2 no descriptor_fms_score_write_reference_pharmacophore_txt no descriptor_fms_score_write_candidate_pharmacophore no descriptor_fms_score_write_matched_pharmacophore no descriptor_fms_score_compare_type overlap descriptor_fms_score_full_match yes descriptor_fms_score_match_rate_weight 5.0 descriptor_fms_score_match_dist_cutoff 1.0 descriptor_fms_score_match_proj_cutoff .7071 descriptor_fms_score_max_score 20 descriptor_fingerprint_ref_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 descriptor_hms_score_ref_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 descriptor_hms_score_matching_coeff -5 descriptor_hms_score_rmsd_coeff 1 descriptor_volume_score_reference_mol2_filename ../004.dock/2p16.lig.min_scored.mol2 descriptor_volume_score_overlap_compute_method analytical descriptor_weight_fps_score 1 descriptor_weight_pharmacophore_score 1 descriptor_weight_fingerprint_tanimoto -1 descriptor_weight_hms_score 1 descriptor_weight_volume_overlap_score -1 gbsa_zou_score_secondary no gbsa_hawkins_score_secondary no SASA_score_secondary no amber_score_secondary no minimize_ligand no atom_model all vdw_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/vdw_AMBER_parm99.defn flex_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex.defn flex_drive_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/flex_drive.tbl chem_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/chem.defn pharmacophore_defn_file /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/parameters/ph4.defn ligand_outfile_prefix 2p16_rescored.out write_footprints yes write_hbonds yes write_orientations no num_scored_conformers 1 rank_ligands no
This is going to be a larger job, so you should run this parallelized on Seawulf:
vi rescore.sh
Here’s another example slurm batch file that should cover the running of your job:
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --time=4:00:00 #SBATCH --nodes=2 #SBATCH --ntasks=28 #SBATCH --job-name=2p16_VS_rescore #SBATCH --output=log_2p16_rescore.txt #SBATCH -p short-28core cd $SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR mpirun -np 56 /gpfs/projects/AMS536/zzz.programs/dock6.10/bin/dock6.mpi -i rescore.in -o rescore.out
Once saved, submit it to Slurm via:
sbatch rescore.sh
Each core will produce its own .out output file, but the only rescore.out file of importance will be the unnumbered rescore.out. However, the “xxxx_rescored.out_scored.mol2” will contain all of the scored ligands, along with all of their descriptor scores. There will also be “xxx_rescored.out_descriptor_scored.txt” files that provide more details about the ligands, including potential hydrogen bonding interactions and footprints. These files should be transferred over to your local computer for viewing within Chimera via ViewDock, along with “xxxx_rescored.out_scored.mol2”.