Difference between revisions of "2023 DOCK tutorial 1 with PDBID 4S0V"
Stonybrook (talk | contribs) (→Downloading a protein from the PDB database) |
Stonybrook (talk | contribs) (→Preparation of the ligand and protein) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
= Preparation of the ligand and protein = | = Preparation of the ligand and protein = | ||
| + | The following steps will show you how to prepare the protein and ligand structures to be used with DOCK. From this point onward, all steps will be done using Chimera. If you are unfamiliar with Chimaera, please see our tutorials here. These steps are very important - if your initial structure is not prepared properly, all downstream analysis can potentially be incorrect. This section will show you how to: | ||
| + | #Evaluate the structure to determine if there are any missing loops/water molecules to be removed/ions that need to be removed | ||
| + | #How to prepare the protein structure | ||
| + | #How to prepare the ligand structure | ||
| + | |||
=== Evaluating the Structure=== | === Evaluating the Structure=== | ||
| + | When evaluating the overall protein/ligand complex, the first thing to look for is missing loops. A missing loop will be indicated by a dashed line in the structure: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 42: | Line 50: | ||
===Checking Hydrogen Atoms and Atom Charges=== | ===Checking Hydrogen Atoms and Atom Charges=== | ||
| − | |||
=Creating the Protein Binding Site Surface= | =Creating the Protein Binding Site Surface= | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 18 February 2023
Contents
Introduction
This tutorial will walk you through the steps necessary for using the DOCK software package. Many drugs are small molecular compounds that attach, or bind, to a protein in our bodies to change how that protein functions. By changing the function of a protein we can treat disease and help people manage symptoms of disorders. Traditionally drug discovery was done through a type of "trial and error" process called High Throughput Screening. Scientists would chemically make, or buy, thousands of small compounds and expose them to cells. They would then observe how the cells responded, either favorably/unfavorably/no effect. This method is time consuming and expensive. It would be better if the scientific community could "virtually screen" these molecules using a computer before creating/buying them - thereby focusing the cost and effort on those which showed the most promising computational results. The DOCK software brings this drug discovery process into the 21st century and uses computers to bind these small molecular compounds to a protein and evaluate the results. DOCK uses algorithms to bring together the small molecule, known as the ligand, and the larger protein, and "DOCK" them together. Our tutorial will walk you through preparing a protein and ligand for docking using an example complex from the protein data bank (https://www.rcsb.org/), complex # 4S0V.
The following steps will be followed:
- Setting up your environmnet
- Downloading a protein from the PDB database
- Determining if there are any missing loops and if they need to be modeled
- Preparing the ligand
- Preparing the protein
Learning Objectives
- Understand why DOCK was created and its current role in drug design
- Gain the ability perform virtual screening of small molecular compounds to a protein from the Protein Data Base (https://www.rcsb.org/)
Setting Up Your Environment
TK
Downloading a protein from the PDB database
To begin we need to download protein complex #4S0V from the PDB. The right side of the top banner has a search bar:
.Simply type 4S0V into the search bar and the protein complex will be displayed.
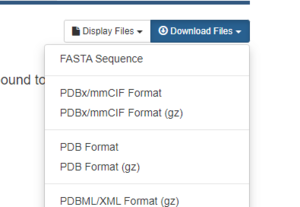
On the right hand side, click on Download Files, then PDB Format.
That's it! The pdb file that we will be working with is now downloaded onto your local computer.
Preparation of the ligand and protein
The following steps will show you how to prepare the protein and ligand structures to be used with DOCK. From this point onward, all steps will be done using Chimera. If you are unfamiliar with Chimaera, please see our tutorials here. These steps are very important - if your initial structure is not prepared properly, all downstream analysis can potentially be incorrect. This section will show you how to:
- Evaluate the structure to determine if there are any missing loops/water molecules to be removed/ions that need to be removed
- How to prepare the protein structure
- How to prepare the ligand structure
Evaluating the Structure
When evaluating the overall protein/ligand complex, the first thing to look for is missing loops. A missing loop will be indicated by a dashed line in the structure: