Difference between revisions of "Test Set Construction SB2024 V1 DOCK6.10 A"
(→H. Interpreting Bookkeeping Spreadsheet) |
(→H. Interpreting Bookkeeping Spreadsheet) |
||
| Line 187: | Line 187: | ||
Likewise now sort from largest to smallest on the "DCEsum" column. If any system has a positive score, treat is as the former step (check for errors, otherwise reject). | Likewise now sort from largest to smallest on the "DCEsum" column. If any system has a positive score, treat is as the former step (check for errors, otherwise reject). | ||
| − | Below is an example of a balanced system. In the first column "O 1" indicates there is 1 additional Oxygen atom in ${pdb_id}.rec.clean.mol2 than the initial file ${pdb_id}.rec.foramber.pdb | + | Below is an example of a balanced system. In the first column "O 1" indicates there is 1 additional Oxygen atom in ${pdb_id}.rec.clean.mol2 than the initial file ${pdb_id}.rec.foramber.pdb. This atom was added to an incomplete sidechain by Amber. |
[[Image:bookkeep_1_ccorbo.png|thumb|center|950px|Spreadsheet sample with Oxygen added to incomplete sidechain]] | [[Image:bookkeep_1_ccorbo.png|thumb|center|950px|Spreadsheet sample with Oxygen added to incomplete sidechain]] | ||
Revision as of 12:01, 19 February 2024
!!!!!!Under Construction!!!!!!
The purpose of this tutorial is to develop a uniform method for adding systems to the Rizzo Lab test set, and rebuilding the set from initial files. This is the protocol to be used by all lab members. If the protocol is changed, a new tutorial should be made, preserving this tutorial.
Contents
- 1 I.Introduction
- 2 II.Scripts for System Preparation
- 3 A. Preliminary File Preparation
- 4 B. Ligand Preparation
- 5 C. Receptor Preparation
- 6 D. Sphere Generation
- 7 E. Single Grid Generation
- 8 F. Multi Grid Generation
- 9 G. Bookkeeping of Heavy Atoms
- 10 H. Interpreting Bookkeeping Spreadsheet
- 11 III.Test Cases for Preparation Integrity
- 12 IV.To Do
I.Introduction
A key development for this tutorial is bookkeeping scripts to manage the count of heavy atoms during processing and indicate unaccounted changes (II.G). Test cases are also included which should be visually inspected for indicated elements to be sure that processing occurred as expected (III).
It is critical ALL of these steps are completed.
II.Scripts for System Preparation
Each script should process the system in a fully automated manner. These scripts are located at:
https://github.com/rizzolab/Testset_Protocols.git
There are key elements to check after each script before proceeding to the next. The output to be checked from each step is written to a folder "zzz.outfiles" with a unique file for each system, at each step. At the top of this file is the netid of the user who ran each process.
These scripts are designed to run in parallel on an HPC. Each step below has approximate timing indicated. If running 100 structures on a step with a timing of 10 minutes, at least 1000 cpu-minutes should be requested. There are averages and individual systems may take much less or more time.
A. Preliminary File Preparation
The receptor and ligand should be prepared from the initial PDB file as outlined in student provided VS tutorials
https://ringo.ams.stonybrook.edu/index.php/Tutorials
Briefly:
(1) The ligand should have hydrogens added with careful attention to protonation state and gasteiger charges added. The extracted ligand is saved as "${pdb_id}.lig.moe.mol2".
(2) The receptor is saved in isolation. Generally any water molecules are deleted, except specialized experiments. Any atomic ions within 8 angstroms of the ligand are retained as part of the receptor. The protocols have prep and frcmod files integrated for Heme cofactors, so these should be retained as part of the receptor. Once the receptor, metal ions, and heme cofactor are extracted they are saved together as "${pdb_id}.rec.foramber.pdb"
(3) Any biologically relevant organic small molecule cofactor (such as NADH / NADPH) other than Heme should be treated as a ligand (1) and saved as "${pdb_id}.cof.moe.mol2".
(4) Files from (1) (2) and (3) should be moved to the folder zzz.master in the upper folder Testset_Protocols from the github repo.
For further clarification, review the student tutorials as indicated.
B. Ligand Preparation
Timing=10 minutes
This step will assign am1bcc charges based on the charge in the preliminary file ${pdb_id}.lig.moe.mol2 and be saved as ${pdb_id}.lig.am1bcc.mol2
In the script submit.run.001.sh, if using a list of PDB codes other than "zzz.lists/clean.systems.all", change this in the script first.
sbatch submit.run.001.sh
After the job has completed check to see if any of the ligands did not process successfully.
bash run.001b.check.sh
Any ligands or cofactors which did not pass will be listed in:
zyy.01.lig_missing.dat / zyy.01.cof_missing.dat
The output for each system is written to file with the netid of the user at the top:
vi zzz.outfiles/${pdb_id}.001.lig.out
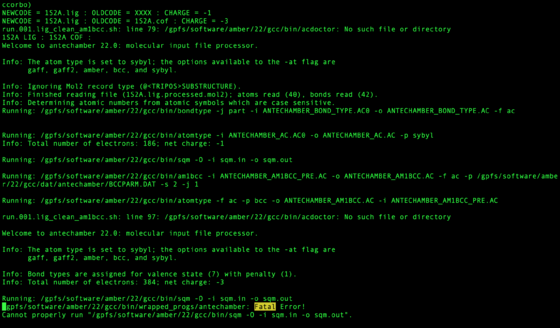
These files should be checked for the phrase Fatal. This may mean the ligand failed or may have another issue. It does not mean with certainty the molecule is wrong, but should be inspected.
grep "Fatal" zzz.outfiles/*001.lig.out
Some cofactors require unexpected bond orders to pass antechamber. If there is a correct version of the cofactor with the same res id such as "NAP" in zzz.master which passes antechamber, use this as a template.
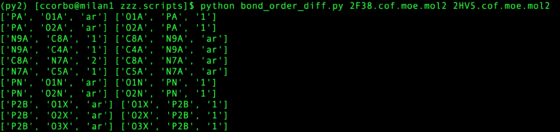
python zzz.scripts/bond_order_diff.py ${pdb_id_1}.cof.moe.mol2 ${pdb_id_2}.cof.moe.mol2
This assumes atom names are equivalent for the mol2 (Hydrogen can be disregarded). Any bonds with different orders are printed, preserving the order input at command line (first argument prints on left, second argument prints on right). The script does not fix the bond orders for you, but helps quickly assigns how to match template.
Other common problems are with carboxylic acid and nitro functional groups. It is best to assign these functional groups "ar" bond types.
C. Receptor Preparation
Timing=1 minute
sbatch submit.run.002.sh
After completion check for missing systems:
bash run.002b.check.sh
Any complexes which did not pass will be listed in:
zyy.02.rec_missing.dat
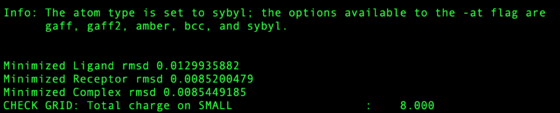
Check the output file for any large RMSD from amber minimization. Restraints in this step are set high so any RMSD > 0.5 Angstroms should be considered dubious. Any structure RMSD > 2.0 Angstroms should be rejected from the test set.
Due to an error in an Amber translation table P.3 atoms are converted to C.3 atoms in cofactors when written to ${pdb_id}.rec.clean.mol2. At this point it is currently corrected manually, but is to be corrected in Amber23. This includes but not restricted to cofactors "NAP","NAD","NDP". If not using Amber23, please check "COF" ${pdb_id}.rec.clean.mol2 to fix these cases.
D. Sphere Generation
Timing=1 minute
sbatch submit.run.003.sh
After completion check for missing systems:
bash run.003b.check.sh
Any systems which did not pass will be listed in:
zyy.03.sph_missing.dat
E. Single Grid Generation
Timing=15 minutes
sbatch submit.run.004.sh
After completion check for missing systems:
bash run.004b.check.sh
Any systems which did not pass will be listed in:
zyy.04.grd_missing.dat
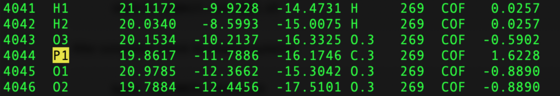
It should be checked that monoatomic ions were successfully integrated into the grid. Changes in naming could cause issues.
vi ${pdb_id}/004.grid/grid.out
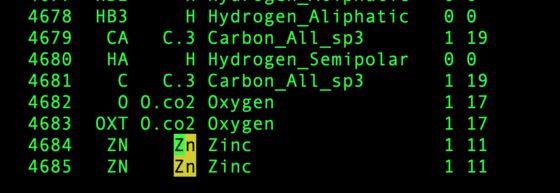
For example, there are 2 Zinc ions expected in the structure 5UPG:
F. Multi Grid Generation
Timing=15 minutes
sbatch submit.run.005.sh
After completion check for missing systems:
bash run.005b.check.sh
Any systems which did not pass will be listed in:
zyy.05.mgr_missing.dat
G. Bookkeeping of Heavy Atoms
Bookkeeping scripts are to account the count of heavy atoms in the initial files compared to final processed files. There are changes to the receptor during processing which are accounted for. This includes: (I) Heavy atoms added to incomplete residues (II) Dual Occupancy atoms deleted (III) Defined mutation from non-standard residue to standard residue. If all atoms are accounted for, the Overall Balance should be 0. Any system that is unbalanced should be inspected.
There are a minority of false positives that have an Overall Balance not equal to 0: (I) Monoatomic ions other than Zn, Mg, Ca come up unbalanced (II) Some pdb have merged columns (ie residue number and x-coordinates do not have space in between) (III) "N" in Heme creates unaccounted change of -4 (IV) Some nonstandard residues outside the active site are mutated to alanine, which is considered an unaccounted change.
To crosscheck with previous built spreadsheet:
(Put downloadable spreadsheet)
UCSF Chimera must be loadable as a module to run bookkeeping scripts!
However any method to convert pdb to mol2 can be used instead.
Run the following 3 commands only after the previous has finished.
sbatch run.006.bookkeeping.sh
sbatch run.006b.merge_bookkeeping.sh
sbatch run.007.system_stats.sh
Create version of zzz.lists/clean.systems.all which had header "sys"
vi zzz.lists/clean.systems.all.header
sys
PDB1
PDB2
PDB3
The 3 files zzz.lists/clean.systems.all.header tmp1.csv and atmcounts_all.csv should all be the same number of lines.
bash run.008.merge_spreadsheet.sh
This produces the final bookkeeping spreadsheet.
H. Interpreting Bookkeeping Spreadsheet
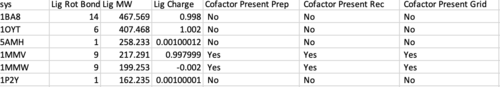
The first column that should be checked is "Cofactor Present Prep","Cofactor Present Rec" and "Cofactor Present Grid". These are associated with the files: ${pdb_id}.cof.moe.mol2 , ${pdb_id}.rec.clean.mol2 and grid.out , respectively. If all 3 columns are not in agreement for a given system, something is wrong.
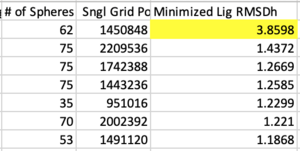
Next sort from largest to smallest on the "Minimized Lig RMSDh" column. This is associated with the file ${pdb_id}.lig.python.min.mol2 . If any system has an RMSD > 2.0 Angstroms it should first be inspected that the ligand and receptor zzz.master files are both in the correct frame. Otherwise the systems should be rejected from the test set, if there is no other error in preparation.
Likewise now sort from largest to smallest on the "DCEsum" column. If any system has a positive score, treat is as the former step (check for errors, otherwise reject).
Below is an example of a balanced system. In the first column "O 1" indicates there is 1 additional Oxygen atom in ${pdb_id}.rec.clean.mol2 than the initial file ${pdb_id}.rec.foramber.pdb. This atom was added to an incomplete sidechain by Amber.
III.Test Cases for Preparation Integrity
These are cases which that need to be visually inspected to ensure key operations during preparation were executed. This step is crucial after building the test set in batch mode.
| System | Element | Details |
|---|---|---|
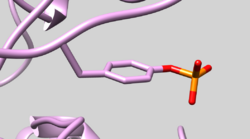
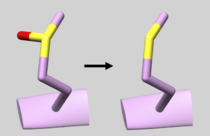
| 2GQG | Phosphotyrosine Residue | Check Residue 171 correctly has Y2P Phosphotyrosine (See Picture below) |
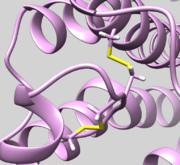
| 2Y03 | Disulfide Bond | Check bond Residue 82.SG and Residue 167.SG is actually bonded (See Picture below ) |
| 4WMZ | Heme | Check Heme is correctly incorporated, including Iron (Fe) |
| 1P44 | NADH Cofactor | Make sure cofactor is present in 1P44.rec.clean.mol2 and grid.out as residue "COF" |
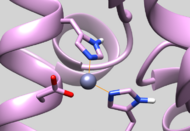
| 5UPG | Zinc Chelated Histidine Protonation | Residue should have HID protonation (See Picture below) |
| 3D94 | NonStandard Residue Defined Mutatation | Make sure Residue 146 successfully mutates to Residue "MET" from "MHO" |
| 1JWT | Long Bonds | Make sure TER is added before long bond in 1JWT.rec.clean.pdb (Dont check mol2). This system should have 4 TER. |
-
-
IV.To Do
1. Integrate prep and frcmod files for cofactors available at http://amber.manchester.ac.uk/ 2. Fix false positives in bookkeeping scripts 3. Add bookkeeping of receptor heavy atoms processed in grid.out
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Tutorial Written By: Christopher Corbo, Rizzo Lab, Stony Brook University (2024)
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>