Difference between revisions of "2025 DOCK tutorial 2 with PDBID 1XMU"
Stonybrook (talk | contribs) (→Surface Sphere Generation) |
Stonybrook (talk | contribs) (→Surface Sphere Generation) |
||
| Line 183: | Line 183: | ||
viii. If successful, the DMS file appears as small dots and align perfectly with the receptor structure. | viii. If successful, the DMS file appears as small dots and align perfectly with the receptor structure. | ||
| − | + | ||
d. Upload dms files to your Seawulf Account | d. Upload dms files to your Seawulf Account | ||
Revision as of 19:01, 8 March 2025
Contents
Introduction
Make 12 directory PDB download version
Structure Preparation
The objectives of this section are:
1. Structural Evaluation
a. Identify any missing loops in the protein structure b. Assess metal coordination atoms for key interactions with the protein
2. Protein Receptor Preparation
a. Generate protein structure in pdb and mol2 format b. Add hydrogen atoms c. Assign appropriate charges d. Save the refined protein structure in mol2 format
3. Ligand Preparation
a. Generate ligand structure in mol2 format b. Add hydrogen atoms c. Assign appropriate charges d. Save the refined ligand structure in mol2 format
4. Alternative method of protein and ligand preparation
a. Using Dock Prep
5. Uploading mol2 Files to your Seawulf Account
a. Transfer via computer terminal using SCP, or b. Transfer via MobaXterm (SFTP)
1. Structural Evaluation
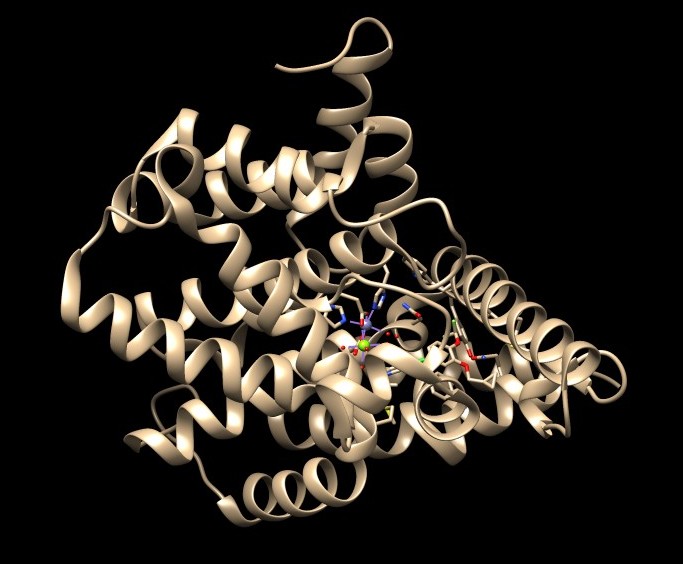
a. Open the downloaded PDB structure in Chimera (In this tutorial, 1XMU). Check for missing loops—these appear as dashed lines in the structure. There are no missing loops in the structure 1XMU, so no further action is needed.
If you find missing loops in your structure, you will need to fix them before proceeding. Refer to (Tutorial 2025 [[1]]) for instructions on fixing missing loops.
b. In 1XMU, there is metal coordination atoms (Zinc and Magnesium) interacting with the protein. It is important to keep them intact and not delete them during protein preparation
2. Protein Receptor Preparation
a. Generate protein structure in pdb and mol2 format
i. Open the downloaded pdb file (1XMU) in Chimera,
ii. Remove ligand: Go to Select → residue → ligand to highlight the ligand
iii. Then, go to Actions → Atoms/Bonds → Delete
iv. Repeat the process to delete water molecules by selecting HOH instead of ligand
v. Save the protein, Go to File → Save Mol2 and save as 1XMU_Rec_nCH.mol2 ('no' Charge and Hydrogen). Also, save the structure in PDB format as 1XMU_Rec_nCH.pdb.
b. Add Hydrogen atoms
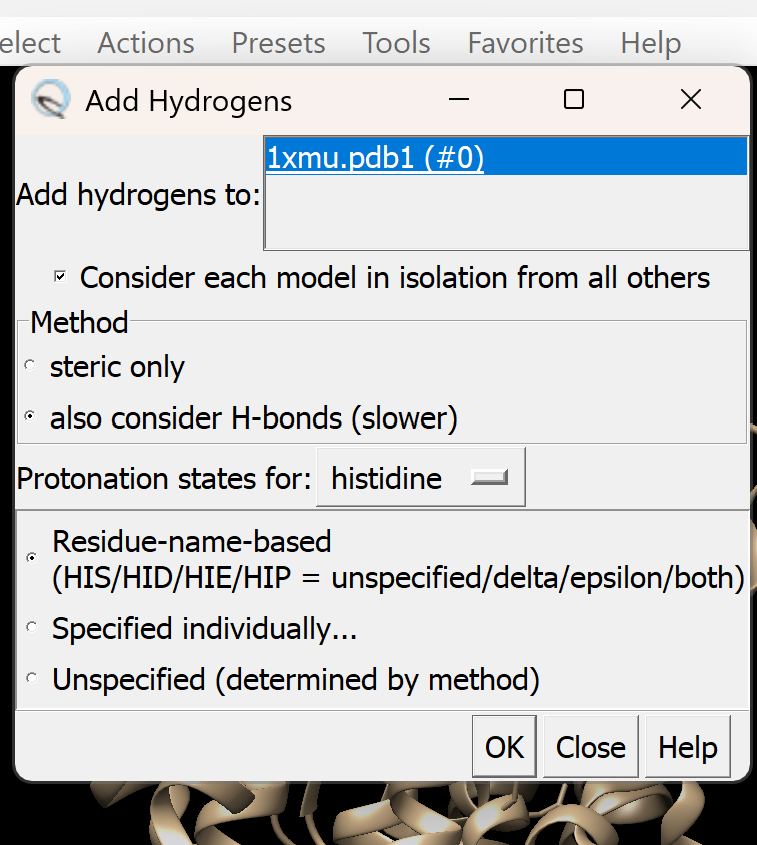
i. Go to Tools → Structure Editing → AddH. A dialogue box like this will appear, adjust as needed
ii. Select OK to proceed. If successful, You will get a confirmation message 'Hydrogens Added'
c. Assign appropriate charges
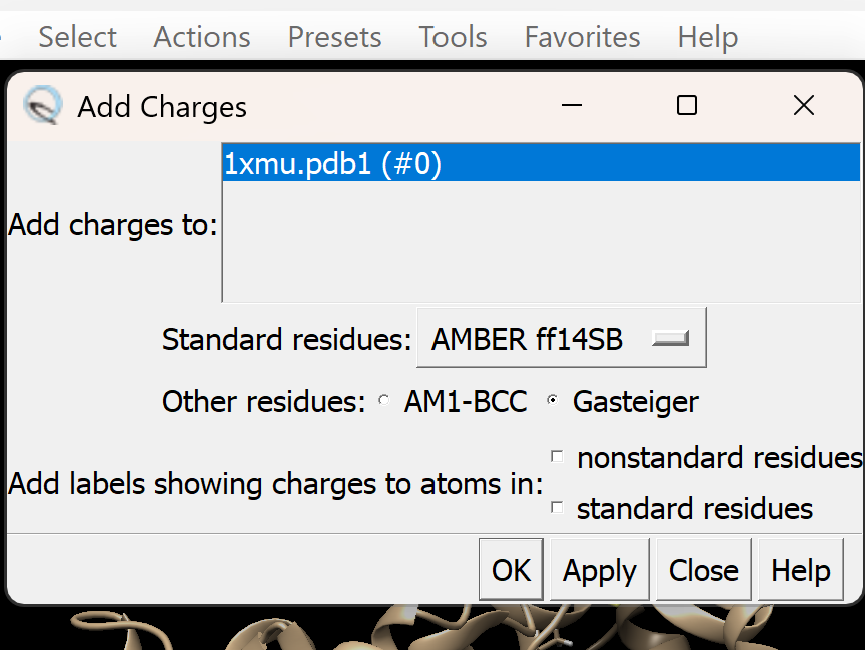
i. Go to Tools → Structure Editing → Add Charge
A dialogue box like this will appear, adjust as needed. For this tutorial, we will use Gasteiger charges. Leave all other settings as they are, then click OK.
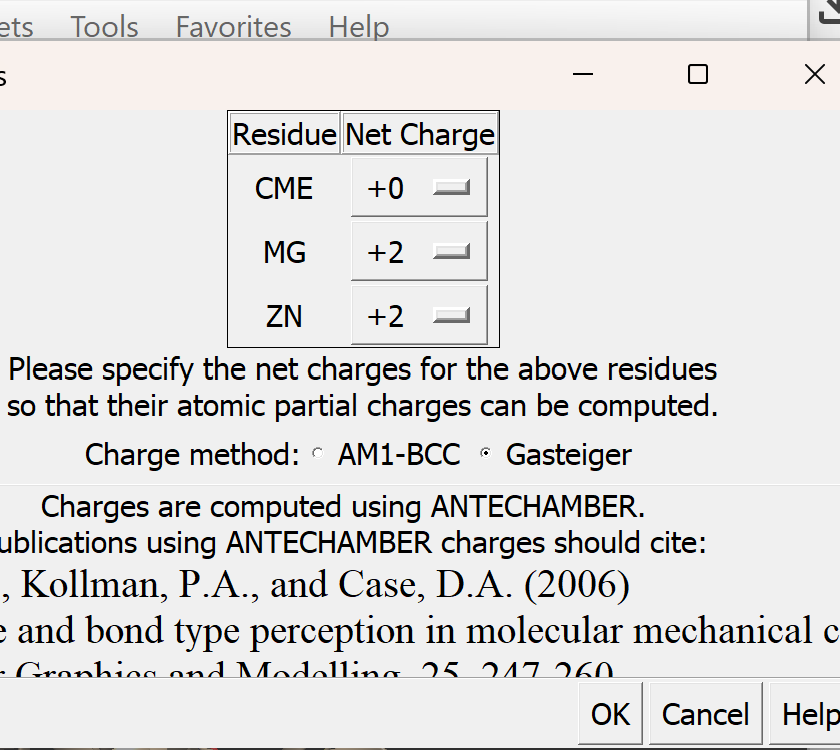
ii. A new pop-up menu will appear
iii. Just as before, make sure that Gasteiger is selected. All other defaults are okay.
iv. Select OK. If successful, You will get a confirmation message 'standard charges added'
d. Go to File → Save Mol2. 1XMU_Rec_wCH.mol2 ('with' Charge and Hydrogen)
3. Ligand Preparation
a. Generate ligand structure in mol2 format
i. Open the downloaded pdb file (1XMU) in Chimera,
ii. Remove protein: Go to Select → residue → ligand to highlight the ligand
iii. Then, go to Select → Invert (selected models)to select everything except the ligand
iv. Go to Actions → Atoms/Bonds → Delete
iv. Save the ligand, Go to File → Save Mol2. 1XMU_lig_nCH.mol2 ('no' Charge and Hydrogen)
b. Add Hydrogen atoms
i. Go to Tools → Structure Editing → AddH
ii. The next menu will be the same as when adding hydrogens during receptor preparation. Use the same settings as before
c. Assign appropriate charges
i. Go to Tools → Structure Editing → Add Charge
ii. The next menu will be the same as when adding hydrogens during receptor preparation. Use the same settings as before
Emphasis: For this tutorial, we will use Gasteiger charge
d. Go to File → Save Mol2. 1XMU_lig_wCH.mol2 ('with' Charge and Hydrogen)
4. Alternative Method for Protein and Ligand Preparation
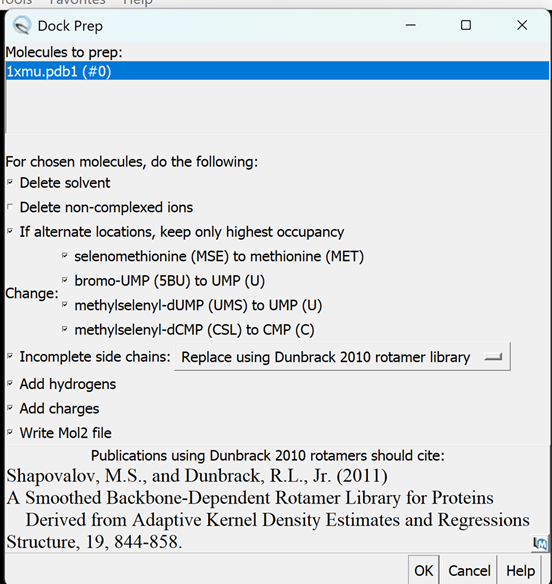
a. Using Dock Prep
This method simplifies preparation by adding hydrogens and assigning charges in a single step.
i. Open the PDB file (1XMU) in Chimera
ii. Isolate the protein and ligand following the steps in Sections 2a and 3a
iii. Go to Tools → Structure Editing → Dock Prep
iv. A pop-up menu will appear – leave all default parameters (as seen below) and click OK
v. The next set of drop-down menus will follow the same process as adding hydrogens and charges manually
vi. The final pop-up menu will be the Save mol2 window
5. Uploading mol2 Files to Your Seawulf Account
a. Transfer via computer terminal using SCP
Use the scp command to transfer files from your local computer to Seawulf: for example,
scp \Users\Documents\1XMU_DOCK_VS\001.structure\1XMU_lig_nCH.mol2 oogunfolakan@milan.seawulf.stonybrook.edu:/gpfs/home/oogunfolakan/1XMU_DOCK_VS/001.structure
NOTE: When using scp via computer terminal, Seawulf automatically pushes DUO authentication to the first registered device i.e you cannot choose which device receives the DUO prompt
b. Transfer via MobaXterm (SFTP)
If you're using MobaXterm, you can upload files directly using the SFTP panel in your SSH browser.
NOTE: Navigate to your target directory (001.structure in this case) on seawulf and drag and drop the files for upload
Surface Sphere Generation
Sphere generation is essential for identifying receptor active sites in DOCK calculations. The objectives of this section are:
1. Write DMS file
a. Generate Receptor Surface b. Generate the DMS file c. Verify the Process d. Upload dms files to your Seawulf Account
2. Run Sphere Generation on Seawulf
1. Write DMS file
a. Generate Receptor Surface
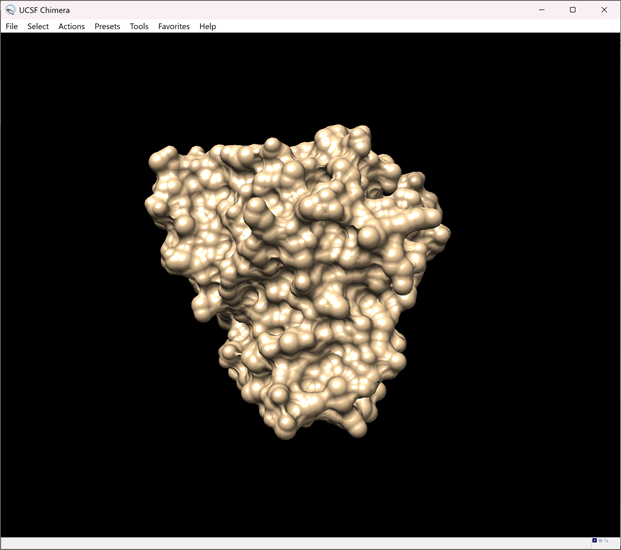
i. Open the Receptor File.pdb (without charges and hydrogens) in Chimera
ii. Go to Actions → Surface → Show
iii. The receptor's surface should now be displayed
b. Generate the DMS file
iv. Go to Tools → Structure Editing → Write DMS
v. A menu to save the file as dms will appear (1XMU_surface.dms)
c. Verify the Process
vi. First of all, Open the 1XMU receptor file.pdb in Chimera
vii. Then, open the 1XMU_spheres.dms file.
viii. If successful, the DMS file appears as small dots and align perfectly with the receptor structure.
d. Upload dms files to your Seawulf Account
ix. On your Seawulf account, move to the 002.surface_spheres directory
x. Use either SCP or MobaXterm (SFTP) to upload 1XMU_spheres.dms as discussed earlier.
2. Run Sphere Generation on Seawulf
i. Open a new file using the command vi INSPH
ii. Type in the following (adjust your file names accordingly)
1XMU_rec_nCH.dms R X 0.0 4.0 1.4 1XMU.sph
iii. save the file and exit
iv. Run sphgen to generate spheres using the command
sphgen -i INSPH -o OUTSPH