Difference between revisions of "2016 AMBER tutorial with Beta Trypsin"
Stonybrook (talk | contribs) (→Antechamber, Parmchk, tLeap) |
Stonybrook (talk | contribs) (→I. Introduction) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Yaping | Yaping | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''AMBER''' | ||
| + | == Headline text == | ||
| + | Amber-Assisted Model Building with Energy Refinement - is a multi-program suite for macromolecular simulations.Amber is distributed in two parts: AmberTools15 and Amber14. You can use AmberTools15 without Amber14, but not vice versa. Amber14 is the most recent version of the software and it includes new force fields such as ff14SB. In addition, in this release, more features from sander have been added to pmemd for both CPU and GPU platforms, including performance improvements, and support for extra points, multi-dimension replica exchange, a Monte Carlo barostat, ScaledMD, Jarzynski sampling, explicit solvent constant pH, GBSA, and hydrogen mass repartitioning. Support is also included for the latest Kepler, Titan and GTX7xx GPUs expanded options for Poisson-Boltzmann solvation calculations, accelerated molecular dynamics, additional features in sander pmemd code, and expanded methods for free energy calculations. Our lab is set up with Amber14 and the latest update of AmberTools14 which contains the programs such as antechamber and tleap to set up your simulation. | ||
| + | The Amber 14 Manual is available to get started with using Amber14. You can search the document for keywords such as "tleap" if you use Adobe Acrobat to view the file. Additionally, AmberTools Reference Manual is another reference for the programs available under Amber tools. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here below are some of the programs available in both Amber and AmberTools: | ||
| + | 1.LEaP: LEaP is an X-windows-based program that provides for basic model building and Amber coordinate parameter/topology input file creation. It includes a molecular editor which allows for building residues and manipulating molecules. | ||
| + | 2.ANTECHAMBER: This program suite automates the process of developing force field descriptors for most organic molecules. It starts with structures (usually in PDB format), and generates files that can be read into LEaP for use in molecular modeling. The force field description that is generated is designed to be compatible with the usual Amber force fields for proteins and nucleic acids. | ||
| + | 3.SANDER: Sander is short for Simulated annealing with NMR-derived energy restraints. This allows for NMR refinement based on NOE-derived distance restraints, torsion angle restraints, and penalty functions based on chemical shifts and NOESY volumes. Sander is also the "main" program used for molecular dynamics simulations, and is also used for replica-exchange, thermodynamic integration, and potential of mean force (PMF) calculations. Sander also includes QM/MM capability. | ||
| + | 4.PMEMD: This is an extensively-modified version (originally by Bob Duke) of the sander program, optimized for periodic, PME simulations, and for GB simulations. It is faster than sander and scales better on parallel machines. | ||
| + | 5.PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: These are used to analyze MD trajectories, computing a variety of things, like RMS deviation from a reference structure, hydrogen bonding analysis, time-correlation functions, diffusional behavior, and so on. | ||
| + | 6.MM_PBSA and MM_PBSA.py: These are scripts that automate post-processing of MD trajectories, to analyze energetics using continuum solvent ideas. It can be used to break energies energies into "pieces" arising from different residues, and to estimate free energy differences between conformational basins. | ||
| + | 7.NAB: Originally named as "nucleic acid builder", NAB is a specialized language for writing programs that manipulate molecules and carry out molecular mechanics or distance-geometry based modeling. NAB provides and interface to Poisson-Boltzmann and RISM integral-equation solvent models. The "amberlite" package uses NAB to study protein-ligand interaction energetics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is also a mailing list available as an additional resource. What you can do with it is: you document your questions and sent to this mail address, some specialists of Amber will be assigned to reply your email and help you. | ||
==II. Structural Preparation== | ==II. Structural Preparation== | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 12 April 2016
For additional Rizzo Lab tutorials see AMBER Tutorials.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to run a molecular dynamics simulation of a protein-ligand complex. We will then post-process that simulation by calculating structural fluctuations (with RMSD) and free energies of binding (MM-GBSA).
Contents
I. Introduction
Yaping
AMBER
Headline text
Amber-Assisted Model Building with Energy Refinement - is a multi-program suite for macromolecular simulations.Amber is distributed in two parts: AmberTools15 and Amber14. You can use AmberTools15 without Amber14, but not vice versa. Amber14 is the most recent version of the software and it includes new force fields such as ff14SB. In addition, in this release, more features from sander have been added to pmemd for both CPU and GPU platforms, including performance improvements, and support for extra points, multi-dimension replica exchange, a Monte Carlo barostat, ScaledMD, Jarzynski sampling, explicit solvent constant pH, GBSA, and hydrogen mass repartitioning. Support is also included for the latest Kepler, Titan and GTX7xx GPUs expanded options for Poisson-Boltzmann solvation calculations, accelerated molecular dynamics, additional features in sander pmemd code, and expanded methods for free energy calculations. Our lab is set up with Amber14 and the latest update of AmberTools14 which contains the programs such as antechamber and tleap to set up your simulation. The Amber 14 Manual is available to get started with using Amber14. You can search the document for keywords such as "tleap" if you use Adobe Acrobat to view the file. Additionally, AmberTools Reference Manual is another reference for the programs available under Amber tools.
Here below are some of the programs available in both Amber and AmberTools: 1.LEaP: LEaP is an X-windows-based program that provides for basic model building and Amber coordinate parameter/topology input file creation. It includes a molecular editor which allows for building residues and manipulating molecules. 2.ANTECHAMBER: This program suite automates the process of developing force field descriptors for most organic molecules. It starts with structures (usually in PDB format), and generates files that can be read into LEaP for use in molecular modeling. The force field description that is generated is designed to be compatible with the usual Amber force fields for proteins and nucleic acids. 3.SANDER: Sander is short for Simulated annealing with NMR-derived energy restraints. This allows for NMR refinement based on NOE-derived distance restraints, torsion angle restraints, and penalty functions based on chemical shifts and NOESY volumes. Sander is also the "main" program used for molecular dynamics simulations, and is also used for replica-exchange, thermodynamic integration, and potential of mean force (PMF) calculations. Sander also includes QM/MM capability. 4.PMEMD: This is an extensively-modified version (originally by Bob Duke) of the sander program, optimized for periodic, PME simulations, and for GB simulations. It is faster than sander and scales better on parallel machines. 5.PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: These are used to analyze MD trajectories, computing a variety of things, like RMS deviation from a reference structure, hydrogen bonding analysis, time-correlation functions, diffusional behavior, and so on. 6.MM_PBSA and MM_PBSA.py: These are scripts that automate post-processing of MD trajectories, to analyze energetics using continuum solvent ideas. It can be used to break energies energies into "pieces" arising from different residues, and to estimate free energy differences between conformational basins. 7.NAB: Originally named as "nucleic acid builder", NAB is a specialized language for writing programs that manipulate molecules and carry out molecular mechanics or distance-geometry based modeling. NAB provides and interface to Poisson-Boltzmann and RISM integral-equation solvent models. The "amberlite" package uses NAB to study protein-ligand interaction energetics.
There is also a mailing list available as an additional resource. What you can do with it is: you document your questions and sent to this mail address, some specialists of Amber will be assigned to reply your email and help you.
II. Structural Preparation
Antechamber, Parmchk, tLeap
Omar, Katie
Antechamber, Parmchk, tLeap
Before beginning the Molecular Dynamics protocol using AMBER, you must first set up your files. In your 001.mol.prep folder, add the following files from your docktutorial directory:
1BJU.lig.mol2 1BJU.rec.noH.pdb
IMPORTANT: delete any headers before the atoms/helix information.
Open 1BJU.rec.noH.pdb
Before running tleap, make a new directory: mkdir 002.ANTE.TLEAP
cp ~/../../tleap.lig.in
- tleap.lig.in
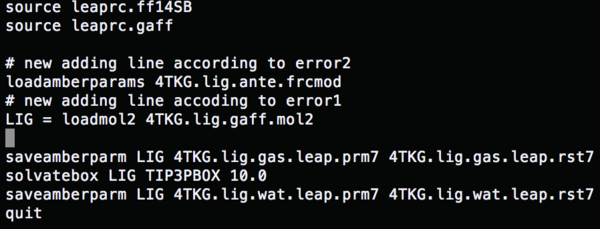
source leaprc.ff14SB #Load a force field source leaprc.gaff LIG = loadmol2 1BJU.lig.mol2 #Conformation file saveamberparm LIG 1BJU.lig.gas.leap.prm7 1BJU.lig.gas.leap.rst7 #Save the ligand gas phase AMBER topology and coordinate file solvatebox LIG TIP3PBOX 10.0 #Solvate the lig using TIP3P, solvent box radii 10 angstroms saveamberparm LIG 1BJU.lig.wat.leap.prm7 1BJU.lig.wat.leap.rst7 #Save the ligand water phase AMBER topology and coordinate files quit
tleap –s –f tleap.lig.in > tleap.lig.out
The atom types which used in '1BJU.lig.mol2' file are not recognized.
So the name of the atoms has to be redefined based on the gaff force field, antechamber can be used to solve the error.
antechamber –i 1BJU.lig.mol2 –fi mol2 –o 1BJU.lig.gaff.mol2 –fo mol2
Change the content of tleap.lig.in to (gaff file)
Re-run tleap:
tleap –s –f tleap.lig.in > tleap.lig.out
So now run parmchk to fix the missing parameters
parmchk –i 1BJU.lig.gaff.mol2 –f mol2 –o 1BJU.lig.ante.frcmod
Change the content of tleap.lig.in to (load amber params) run tleap.lig.in, and all the errors are fixed.
cp ~/../../tleap.rec.in
- tleap.rec.in
source leaprc.ff14SB #Load a force field REC = loadpdb ../001.chimera/1BJU.rec.noH.pdb #Conformation file for receptor saveamberparm REC 1BJU.rec.gas.leap.prm7 4TKG.rec.gas.leap.rst7 #Save the receptor gas phase AMBER topology and coordinate file solvateBox REC TIP3PBOX 10.0 #Solvate the lig using TIP3P, solvent box radii 10 angstroms saveamberparm REC 1BJU.rec.wat.leap.prm7 4TKG.rec.wat.leap.rst7 #Save the receptor water phase AMBER topology and coordinate file quit
tleap –s –f tleap.rec.in > tleap.rec.out
run tleap.rec.in, and all the errors are fixed.
cp ~/../../tleap.com.in tleap –s –f tleap.com.in > tleap.com.out
III. Simulation using pmemd
PMEMD
Agatha, Beilei
MD input file1 01mi.in:
mkdir 01mi.in
01mi.in: equilibration &cntrl imin = 1, maxcyc = 1000, ntmin = 2, ntx = 1, ntc = 1, ntf = 1, ntb = 1, ntp = 0, ntwx = 1000, ntwe = 0, ntpr = 1000, cut = 8.0, ntr = 1, restraintmask = ':1-224 & !@H=', restraint_wt = 5.0,
Copy 01md.in and rename it to 02md.in:
cp 01mi.in 02md.in
02md.in: equilibration &cntrl imin = 0, ntx = 1, irest = 0, nstlim = 50000, temp0 = 298.15, tempi = 298.15, ig = 71287, ntc = 2, ntf = 1, ntt = 1, dt = 0.001, ntb = 2, ntp = 1, tautp = 0.5, taup = 0.5, ntwx = 1000, ntwe = 0, ntwr = 1000, ntpr = 1000, cut = 8.0, iwrap = 1, ntr = 1, nscm = 100, restraintmask = ':1-224 & !@H=', restraint_wt = 5.0,
Using the same way to make 03mi.in, 04mi.in, 05mi.in, 06md.in, 07md.in, 08md.in, 09md.in, 10md.in, 11md.in:
03mi.in: equilibration &cntrl imin = 1, maxcyc = 1000, ntmin = 2, ntx = 1, ntc = 1, ntf = 1, ntb = 1, ntp = 0, ntwx = 1000, ntwe = 0, ntpr = 1000, cut = 8.0, ntr = 1, restraintmask = ':1-224 & !@H=', restraint_wt = 2.0,
04mi.in: equilibration &cntrl imin = 1, maxcyc = 1000, ntmin = 2, ntx = 1, ntc = 1, ntf = 1, ntb = 1, ntp = 0, ntwx = 1000, ntwe = 0, ntpr = 1000, cut = 8.0, ntr = 1, restraintmask = ':1-224 & !@H=', restraint_wt = 0.1,
05mi.in: equilibration &cntrl imin = 1, maxcyc = 1000, ntmin = 2, ntx = 1, ntc = 1, ntf = 1, ntb = 1, ntp = 0, ntwx = 1000, ntwe = 0, ntpr = 1000, cut = 8.0, ntr = 1, restraintmask = ':1-224 & !@H=', restraint_wt = 0.05,
06md.in: equilibration &cntrl imin = 0, ntx = 1, irest = 0, nstlim = 50000, temp0 = 298.15, tempi = 298.15, ig = 71287, ntc = 2, ntf = 1, ntt = 1, dt = 0.001, ntb = 2, ntp = 1, tautp = 0.5, taup = 0.5, ntwx = 1000, ntwe = 0, ntwr = 1000, ntpr = 1000, cut = 8.0, iwrap = 1, ntr = 1, nscm = 100, restraintmask = ':1-224 & !@H=', restraint_wt = 1.0,
07md.in: equilibration &cntrl imin = 0, ntx = 5, irest = 1, nstlim = 50000, temp0 = 298.15, tempi = 298.15, ig = 71287, ntc = 2, ntf = 1, ntt = 1, dt = 0.001, ntb = 2, ntp = 1, tautp = 0.5, taup = 0.5, ntwx = 1000, ntwe = 0, ntwr = 1000, ntpr = 1000, cut = 8.0, iwrap = 1, ntr = 1, nscm = 100, restraintmask = ':1-224 & !@H=', restraint_wt = 0.5,
08md.in: equilibration &cntrl imin = 0, ntx = 5, irest = 1, nstlim = 50000, temp0 = 298.15, tempi = 298.15, ig = 71287, ntc = 2, ntf = 1, ntt = 1, dt = 0.001, ntb = 2, ntp = 1, tautp = 0.5, taup = 0.5, ntwx = 1000, ntwe = 0, ntwr = 1000, ntpr = 1000, cut = 8.0, iwrap = 1, ntr = 1, nscm = 100, restraintmask = ':1-223 & @CA,C,N', restraint_wt = 0.1,
09md.in: equilibration &cntrl imin = 0, ntx = 5, irest = 1, nstlim = 50000, temp0 = 298.15, tempi = 298.15, ig = 71287, ntc = 2, ntf = 1, ntt = 1, dt = 0.001, ntb = 2, ntp = 1, tautp = 0.5, taup = 0.5, ntwx = 1000, ntwe = 0, ntwr = 1000, ntpr = 1000, cut = 8.0, iwrap = 1, ntr = 1, nscm = 100, restraintmask = ':1-223 & @CA,C,N', restraint_wt = 0.1,
10md.in: production &cntrl imin = 0, ntx = 5, irest = 1, nstlim = 500000, temp0 = 298.15, tempi = 298.15, ig = 71287, ntc = 2, ntf = 1, ntt = 1, dt = 0.002, ntb = 2, ntp = 1, tautp = 0.5, taup = 0.5, ntwx = 500, ntwe = 0, ntwr = 500, ntpr = 500, cut = 8.0, iwrap = 1, ntr = 1, nscm = 100, restraintmask = ':1-223 & @CA,C,N', restraint_wt = 0.1,
11md.in: production &cntrl imin = 0, ntx = 5, irest = 1, nstlim = 500000, temp0 = 298.15, tempi = 298.15, ig = 71287, ntc = 2, ntf = 1, ntt = 1, dt = 0.002, ntb = 2, ntp = 1, tautp = 0.5, taup = 0.5, ntwx = 500, ntwe = 0, ntwr = 500, ntpr = 500, cut = 8.0, iwrap = 1, ntr = 1, nscm = 100, restraintmask = ':1-223 & @CA,C,N', restraint_wt = 0.1,
IV. Simulation Analysis
Ptraj
Lauren, Haoyue
ptraj.strip.wat.in:
trajin ../003.PMEMD/10md.trj 1 1000 1 trajin ../003.PMEMD/11md.trj 1 1000 1 trajout 1BJU.trj.strip nobox strip :WAT
ptraj.rec.rmsd.in:
trajin 1BJU.trj.strip trajout 1BJU.com.trj.stripfit reference ../002.ANTE.TLEAP/1BJU.com.gas.leap.rst7 rms reference out 1BJU.rmsd.CA.dat :1-223@CA
ptraj.lig.rmsd.in:
trajin 1BJU.com.trj.stripfit reference ../002.ANTE.TLEAP/1BJU.com.gas.leap.rst7 rms reference out 1BJU.lig.rmsd.dat :224@C*,N*,O*,S* nofit
ptraj.strip.rec.in:
trajin 1BJU.com.trj.stripfit 1 2000 1 trajout 1BJU.lig.trj.stripfit strip :1-223
ptraj.strip.lig.in:
trajin 1BJU.com.trj.stripfit 1 2000 1 trajout 1BJU.rec.trj.stripfit strip :224
ptraj.dist.in:
trajin 1BJU.com.trj.stripfit distance 171OD2_224N1 :171@OD2 :224@N1 out 171OD2_224N1.dat distance 171OD1_224N2 :171@OD1 :224@N2 out 171OD1_224N2.dat
MM-GBSA Energy Calculation
begin by creating a new directory
mkdir 005.MMGBSA/
as well as an input file
vim.gbrescore.in
the following parameters will provide a good estimate of the energy of binding based on solvation enthalpy and binding enthalpy
Single point GB energy calc &cntrl ntf = 1, ntb = 0, ntc = 2, idecomp= 0, igb = 5, saltcon= 0.00, gbsa = 2, surften= 1.0, offset = 0.09, extdiel= 78.5, cut = 99999.0, nsnb = 99999, imin = 5, maxcyc = 1, ncyc = 0, /
We can now submit a job to the cluster we are working on. This script, inside a file named run.sander.rescore.csh , is designed for LIRED, however it can be modified for whatever supercomputer you are working on
#! /bin/tcsh #PBS -l nodes=1:ppn=1 #PBS -l walltime=48:00:00 #PBS -o zzz.qsub.out #PBS -e zzz.qsub.err #PBS -V #PBS -N mmgbsa set workdir = /nfs/guest46/amber_tutorial/005.mmgbsa cd $workdir sander -O -i gb.rescore.in \ -o gb.rescore.out.com \ -p ../002.tleap/4TKG.com.gas.leap.prm7 \ -c ../002.tleap/4TKG.com.gas.leap.rst7 \ -y ../004.ptraj/4TKG.com.trj.stripfit \ -r restrt.com \ -ref ../002.tleap/4TKG.com.gas.leap.rst7 \ -x mdcrd.com \ -inf mdinfo.com
sander -O -i gb.rescore.in \ -o gb.rescore.out.lig \ -p ../002.tleap/4TKG.lig.gas.leap.prm7 \ -c ../002.tleap/4TKG.lig.gas.leap.rst7 \ -y ../004.ptraj/4TKG.lig.trj.stripfit \ -r restrt.lig \ -ref ../002.tleap/4TKG.lig.gas.leap.rst7 \ -x mdcrd.lig \ -inf mdinfo.lig sander -O -i gb.rescore.in \ -o gb.rescore.out.test.rec \ -p ../002.tleap/4TKG.rec.gas.leap.prm7 \ -c ../002.tleap/4TKG.rec.gas.leap.rst7 \ -y ../004.ptraj/4TKG.rec.trj.stripfit \ -r restrt.rec \ -ref ../002.tleap/4TKG.rec.gas.leap.rst7 \ -x mdcrd.rec \ -inf mdinfo.rec exit
Then submit the job as a .csh
qsub run.sander.rescore.csh
Your ligand, receptor, and receptor-ligand complex will all have .out files. The format should look
FINAL RESULTS
NSTEP ENERGY RMS GMAX NAME NUMBER
1 5.9132E+03 2.0005E+01 1.2640E+02 C 159
BOND = 661.8980 ANGLE = 1751.7992 DIHED = 2581.7692
VDWAALS = -1696.6585 EEL = -13958.9335 EGB = -3125.9524
1-4 VDW = 747.0185 1-4 EEL = 7750.8118 RESTRAINT = 0.0000
ESURF = 11201.4791
minimization completed, ENE= 0.59132314E+04 RMS= 0.200047E+02
We can now use a system of equations to elucidate various energies related to our system. VDWAALS = ΔGvdw E(ELS) = ΔGcoulombic E(GB) = ΔGpolar SASA = ESURF
ΔGnonpolar can be estimated by:
ΔGnonpolar = (Solvent Accessible Surface Area)*0.00542 + 0.92
This equation is based on empirical observations relating a molecules surface area and solvation energy
ΔGnonpolar and ΔGmmgbsa are related by anther equation:
ΔGmmgbsa = ΔGvdw + ΔGcoul + ΔGpolar + ΔGnonpolar
all the information needed is in our output files.
ΔΔGbind can now be solved via the equation:
ΔΔGbind = ΔG(mmgbsa complex) – (ΔG(mmgbsa ligand) + ΔG(mmgbsa receptor) (3)
ΔΔGbind is a function of ligand position, so it is useful to plot it. For publications, it is standard protocol to include the mean and standard deviation for your ΔΔGbind.
Lets make a script named get.mmgbsa.csh to extract this sophisticated energetic estimation from the three initial output files of the calculations obtained solve for ΔΔGbind:
bash get.mmgbsa.csh
The output file will be .dat and we can easily use the program xmgrace to plot the information visually
xmgrace MMGBSA_vs_time.dat